
|
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. (000697.SZ): Porter's 5 Forces Analysis |
Fully Editable: Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design: Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Investor-Approved Valuation Models
MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
No Expertise Is Needed; Easy To Follow
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. (000697.SZ) Bundle
In the competitive landscape of aerospace technology, understanding the dynamics at play is crucial for strategic decision-making. Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd. navigates a complex environment influenced by suppliers, customers, and rival firms. From the bargaining power of suppliers to the threat of new entrants, each force presents unique challenges and opportunities. Discover how these elements shape the company's trajectory and impact its market position below.
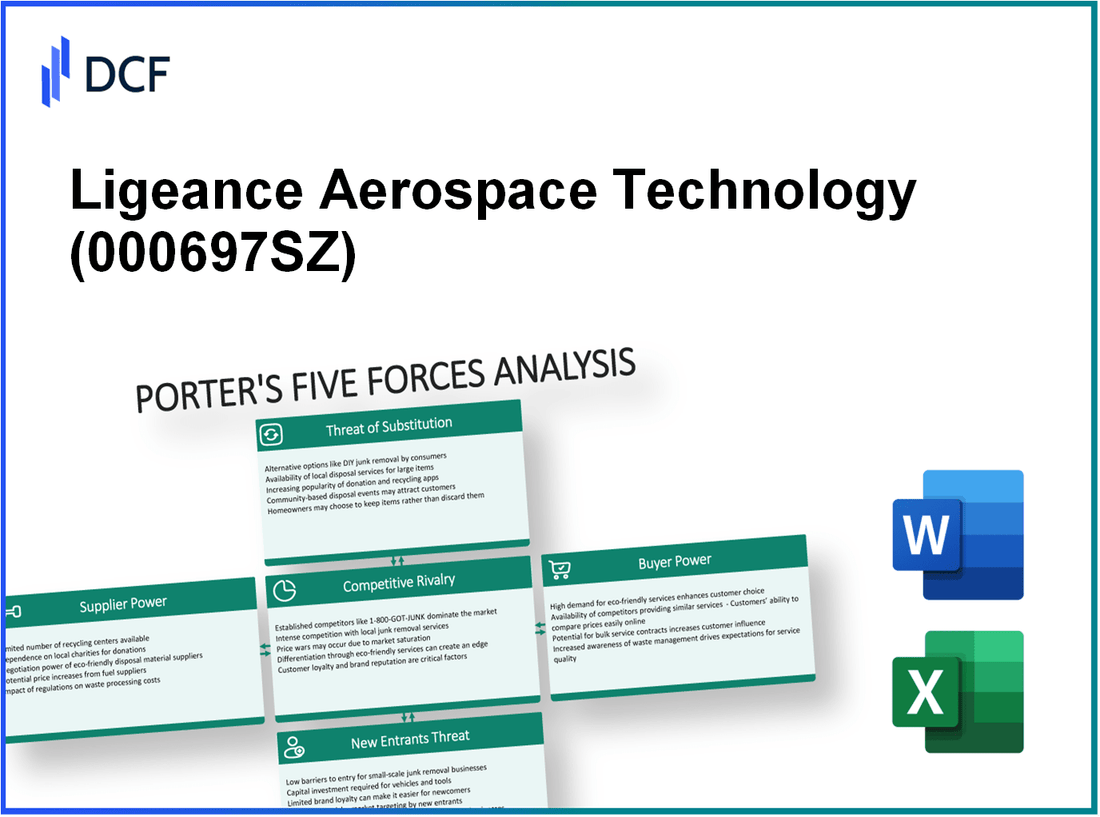
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in the aerospace industry is significantly influenced by various factors, particularly in the context of Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd. This analysis considers the supplier dynamics that affect the company's operational costs and pricing strategies.
Limited number of specialized aerospace suppliers
The aerospace sector relies heavily on a limited number of specialized suppliers for critical components. For example, there are approximately 1,200 suppliers in the global aerospace market, with only a fraction, around 200, providing high-tech aerospace parts. This scarcity provides suppliers with enhanced bargaining power.
High dependency on quality materials and components
Ligeance Aerospace is dependent on quality materials such as titanium and aluminum alloys, which are essential for manufacturing high-performance aircraft components. In 2022, the cost of titanium rose by 30% due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand, enhancing supplier power as companies seek high-quality inputs.
Cost volatility in raw materials impacts price
The volatility in raw material prices is a critical issue for aerospace manufacturers. For instance, in 2023, the price of aluminum surged by 25% compared to 2022 levels, driven by geopolitical tensions and rising energy prices. This fluctuation enables suppliers to impose higher prices, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Vertical integration among suppliers is low
Vertical integration in the aerospace supply chain remains relatively low. Approximately 15% of suppliers are vertically integrated compared to other industries where this figure can reach up to 50%. This lack of integration means that Ligeance must rely on a diverse range of suppliers, further enhancing their negotiating leverage.
High switching costs due to specialized inputs
Switching costs are particularly elevated in aerospace manufacturing due to the specialized nature of inputs. For example, the cost to switch suppliers for high-precision components can exceed $1 million per project. This investment discourages companies like Ligeance from easily changing suppliers, giving existing suppliers more power in negotiations.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | Relevant Data |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Suppliers | High | Approximately 1,200 global aerospace suppliers |
| Dependency on Quality Materials | High | Cost of titanium rose 30% in 2022 |
| Volatility of Raw Material Prices | High | Aluminum price surge of 25% in 2023 |
| Vertical Integration | Low | Only 15% of suppliers are vertically integrated |
| Switching Costs | Very High | Switching costs can exceed $1 million per project |
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of customers
Large aerospace customers possess strong negotiating leverage. Companies such as Boeing and Airbus often have substantial purchasing power due to their size and influence in the aerospace sector. For instance, in 2022, Boeing reported revenues of $62.28 billion, while Airbus recorded revenues of $58.76 billion. This financial muscle allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers, including Ligeance Aerospace.
Demand for customization increases bargaining power. In 2023, the global aerospace market valued at approximately $838 billion is projected to grow. Moreover, the trend towards specialized aerospace components pushes suppliers to meet specific requirements, which enhances the customer's ability to dictate terms. Custom solutions often lead to longer contracts, but also more stringent negotiation processes.
High importance of quality and safety standards cannot be understated. Aerospace components must adhere to rigorous FAA regulations and international standards, such as those outlined by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). The cost of non-compliance can be severe—fines can reach upwards of $5 million, along with potential recalls and reputational damage. This necessitates suppliers to maintain high quality, thereby giving customers leverage to demand lower prices while ensuring compliance.
Limited number of large-scale buyers in the market is another dynamic in customer bargaining power. With only a handful of major commercial aviation clients, such as Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, the concentration of purchasing power is significant. In fact, as of 2023, Lockheed Martin reported a revenue of $65.98 billion, highlighting the economic strength of these buyers. The limited pool of large customers means suppliers compete fiercely for contracts, often leading to more favorable pricing for these key players.
Government contracts can significantly influence power dynamics. In 2022, the U.S. government allocated around $748 billion for defense spending, which directly impacts aerospace technology companies like Ligeance. These contracts can dictate terms and pricing structures, as they often come with extensive compliance requirements. The competitive nature of government contracts gives buyers substantial leverage in negotiations.
| Factor | Details | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Large Aerospace Customers | Boeing: $62.28B, Airbus: $58.76B (2022) | Strong negotiating leverage due to financial weight |
| Demand for Customization | Aerospace market value: $838B (2023) | Increased ability for customers to dictate terms |
| Quality and Safety Standards | Non-compliance fines can exceed $5M | Leverage to demand lower prices while ensuring compliance |
| Limited Buyer Pool | Lockheed Martin revenue: $65.98B (2023) | Higher bargaining power due to concentrated large buyers |
| Government Contracts | U.S. defense spending: $748B (2022) | Significant influence in pricing and contract terms |
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Competitive rivalry
The aerospace industry is characterized by a high level of competitive rivalry, driven primarily by the presence of established aerospace giants such as Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. These companies hold significant market share and resources, making competition fierce. According to a report by MarketResearch.com, the global aerospace and defense market was valued at approximately $838.3 billion in 2021, and expected to grow to $1.03 trillion by 2026.
High fixed costs associated with aerospace manufacturing create a necessity for competitive pricing strategies. Firms often find themselves engaged in price wars, which can compress profit margins. For instance, Boeing reported a net loss of $3.5 billion in 2020 due to reduced demand and increased competition, illustrating how fixed costs can strain financial performance under competitive pressure.
Innovation is essential in distinguishing offerings. Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. invests heavily in R&D, with expenditures around $100 million annually, to develop cutting-edge technologies in avionics and materials science. This focus on differentiation through technology is mirrored across the industry; for example, Airbus allocated approximately $2.5 billion for R&D in 2021, focusing on advancements like sustainable aviation fuels and electric propulsion systems.
The industry growth rate is another factor affecting rivalry intensity. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the aerospace sector is approximately 4.3% from 2021 to 2026. Higher growth rates typically lead to intensified competition as companies race to seize market share. The aerospace industry’s recovery trajectory post-pandemic shows potential, with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) projecting a return to pre-pandemic traffic levels by 2024.
Strategic partnerships and alliances are prevalent in the aerospace sector. For instance, Boeing and NASA have engaged in multiple collaborations aimed at advancing aerospace technologies. Similarly, Ligeance Aerospace is forging alliances with smaller tech firms, emphasizing innovation while sharing the financial burden of R&D. The collaborative aspect reflects a broader trend; according to Deloitte, nearly 70% of aerospace companies reported forming partnerships to enhance competitive advantage in 2022.
| Company | 2021 Revenue | 2020 Net Income | R&D Expenditure | Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boeing | $62.3 billion | -$3.5 billion | $3.2 billion | 39% (estimated) |
| Airbus | $55.8 billion | -$1.1 billion | $2.5 billion | 37% (estimated) |
| Lockheed Martin | $67 billion | $6.8 billion | $1.1 billion | 10% (estimated) |
| Northrop Grumman | $36 billion | $3.1 billion | $1.8 billion | 5% (estimated) |
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes in the aerospace industry significantly impacts Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd.'s business strategy. With the rapid technological advancements and evolving customer preferences, the presence of alternative solutions can pose considerable challenges.
Advanced drone technology as potential substitute
The market for advanced drone technology has expanded dramatically, with the global drone market anticipated to reach a value of $42.8 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 20.5% from $14.1 billion in 2019. Drones are increasingly utilized for various applications like deliveries, surveillance, and agricultural monitoring, which may substitute traditional aerospace services.
Emerging markets for commercial space travel
The commercial space travel sector is gaining traction, projected to grow from $3 billion in 2020 to $30 billion by 2025. Companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin are leading this charge, potentially providing substitutes to conventional aerospace commuting solutions.
Alternative transportation methods for short-distance travel
Short-distance travel alternatives, such as hyperloop systems and electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, are being developed rapidly. The global eVTOL market is estimated to reach $1.6 billion by 2026, providing a novel approach to urban mobility. The short-distance applications of these technologies could threaten traditional aerospace operations.
Continuous innovation reduces substitution risk
Ligeance Aerospace is committed to continuous innovation, with R&D expenditures reaching $50 million in 2022, which represents approximately 10% of its total revenue. This investment positions the company to adapt product offerings and reduce the risk of substitutions through cutting-edge technology and enhanced service capabilities.
Adaptation of sustainability could mitigate threat
As sustainability becomes a focal point, companies that prioritize eco-friendly innovations may have an edge. Ligeance Aerospace has introduced initiatives targeting a 50% reduction in carbon emissions by 2030. This commitment may enhance customer loyalty, reducing the likelihood of substitutive choices based on environmental considerations.
| Substitute Category | Market Size (2025 Estimate) | CAGR (2020-2025) | Current Market Size (2020) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Drone Technology | $42.8 billion | 20.5% | $14.1 billion |
| Commercial Space Travel | $30 billion | N/A | $3 billion |
| eVTOL Market | $1.6 billion | N/A | N/A |
Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co.,Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of new entrants
The aerospace industry exhibits high entry barriers due to significant capital intensity. For instance, the average cost of developing a new commercial aircraft can exceed $10 billion, as seen with programs like the Boeing 777X. This substantial financial requirement deters many potential entrants from entering the market.
In addition to financial constraints, stringent regulatory requirements further complicate market entry. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) impose rigorous safety and certification processes that can take several years and can cost an estimated $1 billion to complete, as noted in reports on aviation compliance. These regulations ensure that only companies that can afford the time and resources to meet these standards can operate effectively in the industry.
There is also strong brand loyalty and established relationships within the aerospace sector. Companies like Boeing and Airbus enjoy long-standing contracts with major airlines and defense entities, often spanning decades. For example, Boeing secured orders worth approximately $23 billion in 2022 alone, indicating the difficulty for new entrants to displace incumbents without significant competitive advantages.
Technology and innovation drive differentiation in the aerospace industry. Ligeance Aerospace, for example, focuses on advanced manufacturing processes and materials that enhance performance and reduce weight, contributing to a competitive edge. The company invested nearly $100 million in R&D in 2023, reflecting the need for ongoing innovation to remain viable against established players.
Economies of scale serve as another hurdle for new entrants. Established firms like Ligeance can spread fixed costs over a large volume of production, resulting in lower per-unit costs. In 2022, Ligeance reported a production increase of 15% while maintaining a gross margin of approximately 20%, demonstrating the advantages of scale that new entrants would struggle to match.
| Factor | Statistical Data | Impact on Entry |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Average cost of new aircraft development: $10 billion | High |
| Regulatory Requirements | Certification costs: $1 billion | High |
| Brand Loyalty | Boeing orders in 2022: $23 billion | High |
| R&D Investment | Ligeance's 2023 R&D: $100 million | Medium |
| Economies of Scale | Production increase in 2022: 15% | High |
Understanding the dynamics of Porter's Five Forces in Ligeance Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd. reveals a complex interplay of supplier dependencies, customer negotiations, and competitive pressures that shape this aerospace player’s strategy. By navigating high entry barriers and evaluating the threats from substitutes and new entrants, Ligeance can leverage its strengths in technology and innovation to enhance its market position while responding effectively to the evolving demands of customers and the competitive landscape.
[right_small]Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
