
|
Aisin Corporation (7259.T): Porter's 5 Forces Analysis |
Fully Editable: Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design: Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Investor-Approved Valuation Models
MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
No Expertise Is Needed; Easy To Follow
Aisin Corporation (7259.T) Bundle
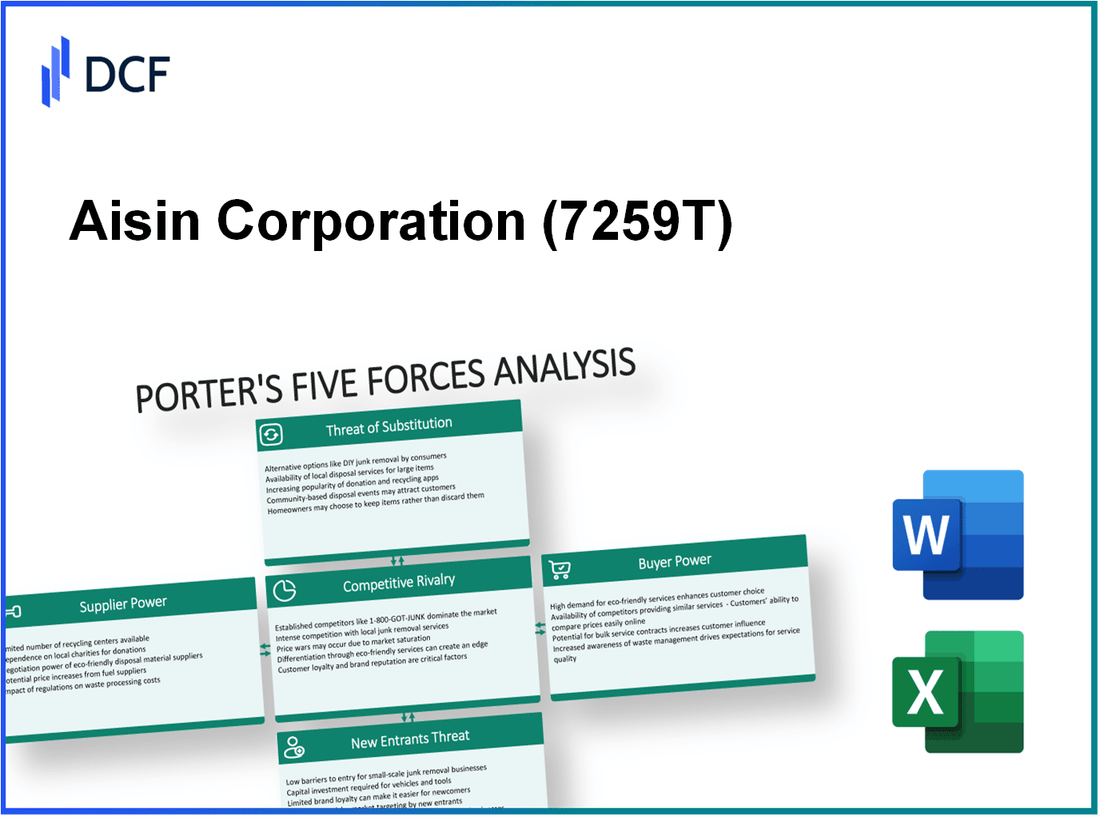
In the competitive landscape of the automotive industry, Aisin Corporation faces multifaceted challenges and opportunities shaped by Michael Porter’s Five Forces Framework. From the bargaining power of specialized suppliers to the threat of new entrants, understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating market complexities. Dive deeper to explore how these forces impact Aisin’s strategies and performance in an ever-evolving sector.
Aisin Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in Aisin Corporation's business environment is significantly influenced by a variety of factors. Aisin, a leading automotive parts manufacturer, operates in a sector characterized by specific supplier dynamics.
High dependency on specialized automotive parts
Aisin Corporation relies heavily on specialized automotive parts that require intricate manufacturing processes. In fiscal year 2022, Aisin's revenue was approximately ¥2.5 trillion, with automotive components accounting for nearly 75% of total sales. This concentration means that suppliers of unique components can exert considerable influence over pricing.
Few suppliers of essential raw materials
The supply chain for critical raw materials, such as steel and plastics, is tightly controlled. As of 2023, the global market for automotive-grade steel alone was valued at around $300 billion, dominated by a few suppliers like ArcelorMittal and Nucor. Their market share allows them to impose price increases without significant competitive threat from alternative suppliers.
Long-term contracts may reduce switching flexibility
Aisin often engages in long-term contracts with suppliers to secure stable prices and quality. In the latest reports, approximately 40% of Aisin's supplier agreements were characterized as long-term contracts. While beneficial for budgeting, this dependency limits Aisin's ability to switch suppliers quickly in response to price changes.
Supplier innovation impacts product development
The automotive industry thrives on innovation, and suppliers play a crucial role in introducing new technologies. In 2022, Aisin invested over ¥100 billion in R&D, emphasizing collaboration with suppliers on innovations such as electric vehicle technologies and advanced safety systems. The suppliers' ability to innovate directly affects Aisin’s competitive positioning and product offerings.
Backward integration potential can reduce supplier power
Aisin has explored backward integration strategies to mitigate supplier power. In 2022, Aisin acquired several specialty material companies, investing over ¥50 billion in these initiatives. This move aims to decrease reliance on external suppliers and enhance control over production costs and quality.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Supplier Power |
|---|---|---|
| Dependency on specialized parts | High reliance on intricate automotive components | Increases supplier influence |
| Few suppliers of raw materials | Limited number of suppliers for essential materials | High bargaining power of suppliers |
| Long-term contracts | Approximately 40% of agreements are long-term | Reduces flexibility to switch |
| Supplier innovation | Invested ¥100 billion in R&D for collaboration | Increases supplier importance |
| Backward integration | ¥50 billion invested in acquisitions | Decreases supplier power |
This analysis of Aisin Corporation's bargaining power of suppliers reveals a complex interplay of dependency, contractual arrangements, and strategic initiatives aimed at mitigating supplier power. The reliance on specialized parts and few raw material suppliers presents challenges, while efforts in innovation and integration provide avenues for reducing this power.
Aisin Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of customers
The bargaining power of customers for Aisin Corporation is significantly influenced by its relationships with major automotive manufacturers. Companies such as Toyota, Honda, and Ford are among the key clients, representing a substantial portion of Aisin's revenues. For instance, in 2022, Toyota accounted for approximately 32% of Aisin’s total sales.
Major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) typically impose high-quality demands, necessitating Aisin to meet rigorous standards. In recent evaluations, Aisin achieved an average quality rating of 98.5%, reflecting excellence in production processes that align with customer specifications.
Price sensitivity among customers can shift according to market dynamics. During economic downturns, automotive companies often seek cost-cutting measures, pressuring suppliers like Aisin to reduce prices. For example, in response to supply chain pressures during 2021, Aisin experienced a 5% decrease in average selling prices as customers negotiated lower costs to maintain profitability.
Customers benefit from alternative sourcing options, as the automotive parts industry is competitive. Aisin competes with major players including Bosch and Denso, which also supply similar components. This competitive landscape enables automotive manufacturers to leverage their position when negotiating contracts, enhancing their bargaining power.
Establishing strong customer relationships is vital for retaining business and securing repeat orders. Aisin invests heavily in relationship management and customer service enhancements. The company noted a 20% increase in contract renewals over the last two years, underscoring the effectiveness of its customer relationship strategies.
| Year | Customer Concentration (% of Total Sales) | Average Quality Rating (%) | Average Price Reduction (%) | Contract Renewal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 38 | 97.5 | -5 | 15 |
| 2022 | 32 | 98.5 | -5 | 20 |
The bargaining power of customers remains a critical aspect of Aisin's business strategy; the company must continuously adapt to maintain competitive pricing while meeting the high standards set by major automotive clients. This dynamic highlights the importance of quality and relationship management in sustaining its market position.
Aisin Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Competitive rivalry
Aisin Corporation operates within a highly competitive landscape, characterized by numerous global automotive component manufacturers. The automotive industry comprises over 30,000 suppliers, leading to intense competition where Aisin must contend with players like Bosch, Delphi Technologies, and Continental. The competitive rivalry is further heightened by the presence of both established firms and emerging players, often specializing in innovative technologies.
Innovation is a critical factor driving competition in this sector, as rapid product evolution occurs due to technological advancements. For instance, as of 2022, the global automotive industry invested approximately $250 billion into research and development, focusing heavily on electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies. Aisin itself has invested about ¥220 billion (approximately $2 billion) in R&D to remain competitive, reflecting the industry's emphasis on continual innovation.
Price wars are prevalent as manufacturers strive for market share, often leading to eroded profit margins. Aisin's gross profit margin was reported at 18.3% in 2022, down from 19.7% in the previous year, as pricing pressures from competitors like Bosch, which reported a gross margin of 20.3%, have intensified. The company's mode of operation often requires balancing competitive pricing with maintaining profitability.
Brand reputation plays a pivotal role in securing a competitive edge. Aisin ranks consistently among the top suppliers in the automotive sector, with a brand value estimated at approximately $3.6 billion. This reputation fosters trust and long-term relationships with major automotive brands, including Toyota and Honda, critical for sustaining its market position.
Direct competition with other Tier 1 suppliers represents another significant aspect of Aisin's competitive environment. Tier 1 suppliers are essential to the OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), and Aisin must effectively differentiate itself from companies such as Denso and Magna International. The table below outlines key financial metrics of Aisin Corporation and its primary Tier 1 competitors.
| Company | Revenue (2022) | Gross Profit Margin (2022) | R&D Investment (2022) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aisin Corporation | ¥1.87 trillion (approx. $17.1 billion) | 18.3% | ¥220 billion (approx. $2 billion) |
| Bosch | €78.7 billion (approx. $85 billion) | 20.3% | €7.5 billion (approx. $8 billion) |
| Denso | ¥5.1 trillion (approx. $46.2 billion) | 20.6% | ¥400 billion (approx. $3.6 billion) |
| Magna International | $37.9 billion | 12.8% | $1.5 billion |
| Delphi Technologies | $3.5 billion | 14.7% | $300 million |
The competitive rivalry faced by Aisin Corporation is multifaceted, with numerous global competitors leveraging innovation, aggressive pricing, and brand reputation to gain market traction. The balance of power shifts continuously as each player seeks to capitalize on new market trends and technological advancements.
Aisin Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes is a significant factor in Aisin Corporation's market environment, affecting its pricing power and market share. This component is especially critical in the automotive sector, where advances and shifting consumer preferences can lead customers to alternative products.
Alternative materials, e.g., lightweight composites
The automotive industry increasingly utilizes lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Aisin Corporation faces competition from composite materials, which have seen a market share growth of approximately 20% annually. For instance, in 2022, the global lightweight materials market for automotive applications was valued at around $95 billion, projected to reach $150 billion by 2026, driven by regulatory pressures and technological advancements.
Technological advancements in electric vehicle components
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more prevalent, the components used in traditional internal combustion engine vehicles face substitution. The global EV components market is expected to grow from $22 billion in 2021 to $70 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25%. Aisin must adapt its product offerings to remain competitive in this rapidly evolving landscape.
OEMs in-house production as a substitute
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are increasingly investing in in-house production capabilities. In 2023, it was reported that leading OEMs like Tesla and Ford are investing around $10 billion and $11 billion respectively in developing in-house manufacturing facilities for critical components, which presents a substantial threat to suppliers such as Aisin. This trend could potentially reduce Aisin's market share and negotiating power.
Evolving consumer preferences towards high-tech solutions
Today's consumers favor high-tech automotive features, leading to increased demand for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and connected vehicle technologies. A report by McKinsey in 2023 noted that about 70% of consumers consider technology features as a key factor in automotive purchase decisions. This could steer them toward alternative manufacturers offering more integrated technology solutions, putting pressure on Aisin's traditional offerings.
Cost-effective alternative solutions from emerging markets
Aisin Corporation also faces competition from suppliers in emerging markets that offer cost-effective substitutes. For instance, Chinese automotive parts manufacturers are seeing a growth trend, with an average price advantage of around 15%-20% compared to established manufacturers. As of 2023, the market for automotive parts in China is valued at approximately $250 billion, with suppliers recognized for their ability to provide lower-cost alternatives without compromising on quality.
| Factor | Details | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Materials | Lightweight composites trending in the automotive sector | Projected market growth from $95 billion in 2022 to $150 billion by 2026 |
| EV Component Technology | Rise in electric vehicle production | EV components market growth from $22 billion in 2021 to $70 billion by 2026 |
| OEM In-house Production | Major OEMs investing heavily in self-sufficiency | Tesla and Ford investing $10 billion and $11 billion respectively |
| Consumer Preferences | Demand for high-tech automotive features | 70% of consumers prioritize technology in their buying decisions |
| Emerging Market Solutions | Cost-effective substitutes from manufacturers in emerging markets | Chinese suppliers offering 15%-20% lower prices |
The dynamics of these five forces underscore the complex environment in which Aisin operates, as the threat of substitutes continuously evolves with market trends and consumer preferences.
Aisin Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of new entrants
The automotive parts industry, where Aisin Corporation operates, faces significant barriers to entry, impacting the threat of new entrants.
High capital investment deters new entrants
The automotive industry requires substantial capital investment. For instance, the average cost to establish a manufacturing facility can vary between $10 million to $300 million depending on the scale and technology utilized. Aisin Corporation reported capital expenditures of approximately $400 million in 2022. This capital intensity discourages new players from entering the market.
Established relationships with OEMs pose entry barriers
Aisin has long-standing relationships with major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) such as Toyota, for which it supplies over 40% of its total sales. New entrants would need to invest considerable time and resources to build similar relationships, which can take years and requires proven product reliability and quality.
Evolving regulatory standards complicate entry
The automotive industry is subject to stringent regulatory standards regarding safety, emissions, and sustainability. Compliance costs can reach upwards of $5 million for new entrants just to meet basic regulatory requirements. In 2021, the European Union introduced new CO2 emission regulations, mandating a reduction of 55% by 2030. This evolving regulatory landscape increases costs and complexity for new market participants.
Economies of scale advantage for incumbents
Aisin benefits from economies of scale, which allows it to lower costs per unit while increasing production. Aisin Corporation had a revenue of approximately $30 billion in the fiscal year ending March 2023. A company needs to reach significant production levels to compete effectively, typically requiring a market share of at least 10% to achieve comparable efficiency.
Technological expertise required for competitive entry
Technological advancements play a critical role in the automotive industry. Aisin Corporation devotes around 6% to 8% of its revenue to R&D annually, translating to over $1.8 billion in research investments for 2022. New entrants in the market must not only have access to capital but also the necessary technical expertise and innovation capabilities to compete effectively in a rapidly evolving sector.
| Factor | Details | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | $10 million to $300 million for a facility | High barrier; large financial commitment needed |
| OEM Relationships | Aisin sells over 40% of sales to Toyota | Time-consuming to develop similar partnerships |
| Regulatory Standards | Compliance costs can exceed $5 million | Complexity and cost raise entry barriers |
| Economies of Scale | Revenue of approx. $30 billion | Need significant market share to compete |
| Technological Expertise | R&D spending of 6% to 8% of revenue | Essential for innovation; limits new entrant capability |
The dynamics of Aisin Corporation’s position in the automotive industry are shaped profoundly by Porter's Five Forces, revealing the intricate balance of power between suppliers, customers, and competitors, while highlighting the significant barriers to entry and threats from substitutes. Understanding these forces not only aids in navigating the complexities of market competition but also emphasizes the strategic decisions that can bolster Aisin's resilience and enable sustainable growth in an ever-evolving landscape.
[right_small]Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
