
|
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. (9119.T): Porter's 5 Forces Analysis |
Fully Editable: Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design: Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Investor-Approved Valuation Models
MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
No Expertise Is Needed; Easy To Follow
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. (9119.T) Bundle
In the dynamic world of shipping, Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. navigates a complex sea of challenges and opportunities shaped by Michael Porter’s Five Forces. From the bargaining power of suppliers and customers to the threats posed by substitutes and new entrants, understanding these forces is crucial for grasping the competitive landscape. Dive deeper to explore how these factors influence not only Iino Kaiun's strategic decisions but also the broader shipping industry.
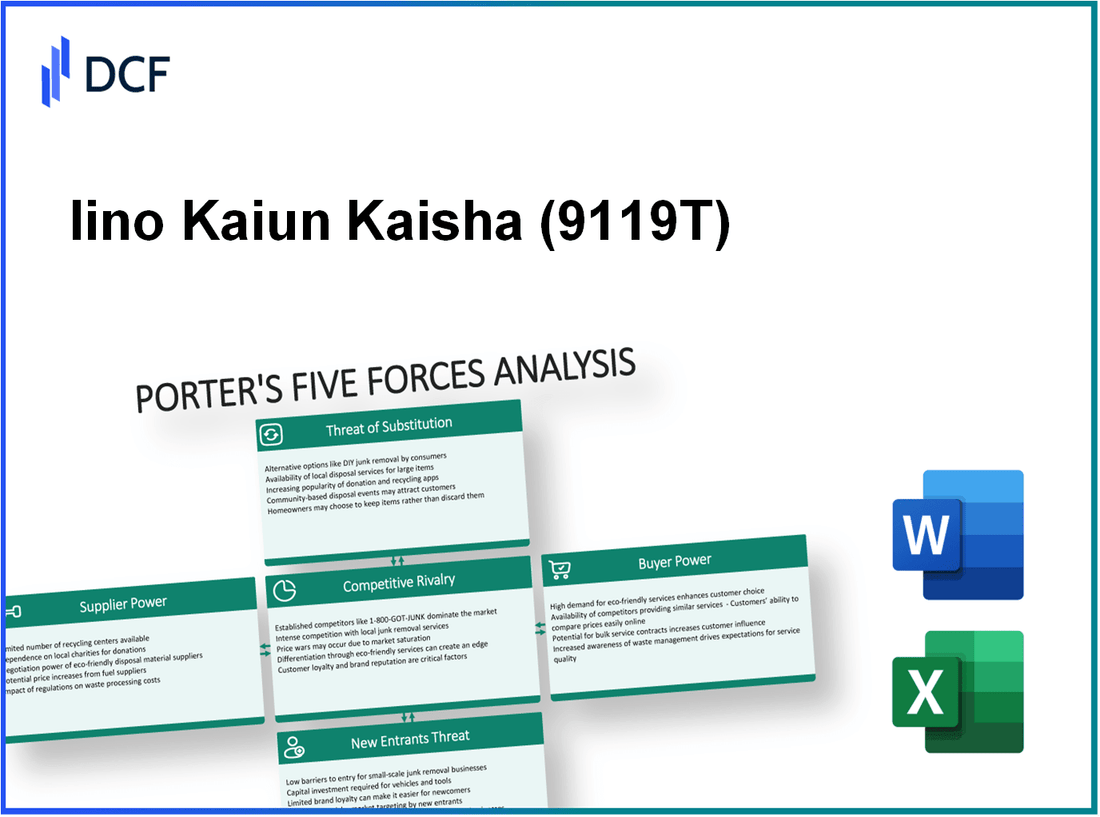
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in the context of Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. can significantly impact operational costs and profitability. Several factors contribute to this power, ranging from the availability of specialized ship manufacturers to the dependency on fuel providers.
Limited specialized ship manufacturers
The market for specialized ship manufacturing is relatively concentrated. As of 2023, only a handful of manufacturers dominate this niche, including major players like Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering and Hyundai Heavy Industries. The limited number of suppliers gives them the power to dictate prices. For instance, the average cost of constructing a large vessel can range from $50 million to $100 million, depending on specifications and suppliers.
Dependency on oil and fuel providers
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. relies heavily on crude oil and fuel suppliers for its shipping operations. As of late 2023, the price of bunker fuel, which is crucial for maritime transportation, has experienced fluctuations, averaging around $600 per metric ton, an increase of approximately 40% compared to 2022. Such dependence on volatile fuel sources enhances supplier power.
Few alternatives for high-quality marine equipment
When it comes to acquiring high-quality marine equipment, options are limited. For instance, Iino Kaiun Kaisha has procured equipment primarily from established brands like Wärtsilä and MAN Energy Solutions. The costs associated with high-quality equipment are substantial; for example, a marine engine can cost upwards of $2 million, reinforcing the suppliers' leverage over pricing.
Strong reputation influences supplier relationships
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, with its long-standing reputation in the shipping industry, has been able to cultivate favorable relationships with its suppliers. This reputation aids in negotiating terms and securing more favorable pricing. In 2023, it was reported that companies with strong reputations for reliability can negotiate prices up to 10%-15% lower than the market rate, thereby influencing overall supplier dynamics.
Long-term contracts stabilize supplier power
The company often engages in long-term contracts with suppliers to ensure stability in pricing and supply. As of 2023, long-term contracts accounted for approximately 70% of Iino Kaiun Kaisha’s procurement activities. This approach mitigates the impact of supplier price increases, providing an element of predictability in cost management.
| Supplier Type | Average Costs | Market Influence | Contract Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ship Manufacturers | $50M - $100M | High | 5-10 years |
| Bunker Fuel Providers | $600/metric ton | Very High | Varies |
| Marine Equipment Suppliers | $2M+ | Moderate | 3-5 years |
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of customers
The bargaining power of customers in the shipping sector, particularly for Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd., is influenced by several key factors.
Large shipping contracts grant negotiation leverage
Companies often engage in large-scale shipping contracts, which can reach totals of several hundred million yen. For example, Iino Kaiun Kaisha's contracts can range significantly, with key contracts exceeding ¥1 billion. These substantial amounts provide customers with significant negotiation power, especially when they offer long-term commitments in exchange for discounted rates.
Availability of multiple shipping companies
The maritime industry is characterized by a high level of competition with over 40,000 registered shipping companies globally. This vast number increases buyer options, allowing them to switch providers easily, thereby enhancing their bargaining power. In Japan alone, according to the Japan Shipowners' Association, the number of operating shipping companies has grown by approximately 3% annually, increasing competitive pressure on firms like Iino Kaiun Kaisha.
Demand for eco-friendly transportation options
With the global shift towards sustainability, customers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly shipping solutions. Reports indicate that approximately 70% of major shipping clients are now prioritizing environmentally sustainable practices in their logistics contracts. This shift compels companies to invest in greener technologies, such as fuel-efficient vessels and carbon offsetting programs, granting buyers further leverage in negotiations.
Increasing expectations for timely deliveries
In an era of rapid delivery expectations, customers now expect shipments within 24-48 hours for local deliveries. A recent survey stated that 65% of customers consider delivery time as a critical factor in choosing a shipping provider. Insufficient adherence to these expectations can lead to penalties and loss of contracts, further empowering customers in negotiations.
Client diversity reduces dependency on a few key customers
Iino Kaiun Kaisha has diversified its client base across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, and industrial goods. This diversification strategy results in reduced dependency on a few key clients, with the largest customer accounting for less than 15% of total revenue. This broad client portfolio dilutes individual customer power, although it also adds complexity to managing client demands and expectations.
| Factor | Details | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Large shipping contracts | Potential contract values > ¥1 billion | High |
| Availability of shipping companies | Over 40,000 registered companies globally | High |
| Demand for eco-friendly solutions | 70% of clients prioritize sustainability | Increases |
| Timely deliveries | Expectations for 24-48 hour delivery | High |
| Client diversity | Largest client < 15% of revenue | Moderate |
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Competitive rivalry
The competitive landscape for Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd., a key player in the shipping industry, is characterized by intense rivalry among several formidable competitors. The shipping sector is dominated by major global players, which heightens competition significantly.
High competition from global shipping giants: The shipping market features significant players such as A.P. Moller-Maersk, MSC, and Hapag-Lloyd. A.P. Moller-Maersk reported a revenue of approximately $61.8 billion for the fiscal year 2022, while MSC holds about 17% of the global container shipping market share as of 2023. This competitive pressure challenges Iino Kaiun's market positioning and pricing strategies.
Price wars due to commoditized services: The shipping industry often operates on thin margins, leading to fierce price competition. The global average freight rate has fluctuated, with a recent drop of approximately 30% from its peak in 2021, affecting profitability across the board. Companies are compelled to reduce prices to maintain volume, impacting Iino Kaiun’s revenue streams.
Brand loyalty plays minor role: In the highly commoditized shipping industry, brand loyalty is less pronounced. A survey indicated that 72% of shippers prioritize cost over brand when selecting shipping partners. This situation compels Iino Kaiun and others to compete primarily on price and service efficiency rather than brand recognition.
Market share constantly contested: Iino Kaiun, while established, faces challenges in maintaining its market share. In 2022, it held a market share of approximately 1.2% in Japan's shipping industry. However, the ongoing entry of new players and expansion of existing competitors is causing fluctuations in market share, indicating an unstable competitive environment.
Innovation in shipping technology differentiates companies: Technological advancement is critical in distinguishing competitors. Companies investing in eco-friendly ships, such as Maersk's order of 8 new dual-fuel ships costing around $1.4 billion, are setting new industry standards. Iino Kaiun must keep pace with innovations like automation and fuel efficiency enhancements to remain competitive.
| Company | 2022 Revenue (in billion USD) | Market Share (%) | New Vessels Ordered (2022) | Average Freight Rate Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A.P. Moller-Maersk | 61.8 | 17 | 8 | -30 |
| MSC | 58.0 (estimated) | 17 | 15 | -30 |
| Hapag-Lloyd | 25.2 | 9 | 6 | -30 |
| Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. | 1.2 | 1.2 | 2 | -30 |
This competitive rivalry framework highlights the challenges faced by Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. in navigating a complex and dynamic market environment. As the shipping industry continues to evolve, the ability to adapt and innovate will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes significantly impacts Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd., especially as the logistics and shipping landscape evolves. As the company operates primarily in the maritime transport sector, understanding alternatives is crucial for assessing competitive pressures.
Air freight as a quicker alternative
Air freight services are often viewed as a direct substitute for maritime transport due to their speed. In 2022, the global air freight market was valued at approximately $128.9 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% through 2030. The average time for air shipments is less than 24 hours compared to several days for sea transport, making air freight particularly appealing for high-value or perishable goods.
Rail and road transport for shorter distances
For shorter distances, rail and road transport represents a competitive alternative to shipping. In 2023, the rail freight transport market in Japan accounted for approximately ¥1.9 trillion (around $14.1 billion). Road freight is also significant, with the market size estimated at ¥6.1 trillion (approximately $45 billion) in Japan, offering the flexibility and speed that shipping cannot match for local deliveries.
Digital goods reducing need for physical shipping
The rise of digital goods is also a key factor reducing demand for physical shipping. The global digital goods market, which includes software, e-books, and streaming services, is expected to reach $363 billion by 2024, limiting the need for transport services for traditional goods.
Environmental concerns pushing for greener methods
Increasing environmental awareness is driving businesses to seek greener shipping alternatives. According to a 2022 report, 72% of consumers are more likely to purchase from companies demonstrating sustainable practices. Additionally, the carbon emissions from shipping are estimated to contribute 3% to 4% of total global greenhouse gas emissions, prompting shippers to consider alternatives like rail or renewable energy vehicles.
Regulatory changes prompting alternative logistics
Regulatory shifts are also impacting the logistics landscape. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set regulations aiming for a 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by 2050, pushing companies to evaluate alternatives such as electric vehicles and rail transport. In 2023, over 20% of shipping companies reported initiating changes to comply with anticipated regulations.
Comparative Analysis of Transport Modes
| Transport Mode | Average Cost per Tonne-Kilometer | Average Delivery Time | Market Growth Rate (CAGR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Freight | $0.80 | 1 day | 6.3% |
| Rail Freight | $0.04 | 3-5 days | 3.5% |
| Road Freight | $0.20 | 1-3 days | 4.2% |
| Sea Freight | $0.10 | 7-14 days | 3% |
These insights highlight the competitive dynamics facing Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. as it navigates the increasing threat of substitutes in the logistics industry.
Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of new entrants
The shipping industry, particularly in Japan, presents significant barriers to entry for potential new entrants, particularly in the context of Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd.
High capital investment discourages new players
Entering the maritime transport sector requires substantial financial outlay. The average cost of a new bulk carrier ship is approximately $50 million to $100 million. This figure can vary significantly based on the size and specifications of the vessel. In addition to the ships themselves, new companies must also invest in terminals, vessels, and compliance with safety standards.
Stringent regulatory compliance required
Shipping companies must adhere to strict international regulations, including the International Maritime Organization (IMO) standards. Compliance can lead to costs ranging from $1 million to $5 million annually for certification, training, and maintaining safety protocols. Non-compliance may result in heavy fines or the discontinuation of operations.
Established networks and relationships as barriers
Iino Kaiun Kaisha benefits from long-standing relationships with suppliers, customers, and ports. These connections are essential for securing contracts and operational efficiency. According to recent data, approximately 70% of new entrants fail to establish adequate commercial relationships within their first five years due to the competition posed by established entities like Iino Kaiun Kaisha.
Technology adoption necessary for operational efficiency
In the current landscape, technological advancements play a crucial role. New entrants are required to adopt innovative technologies such as fleet management systems and automated processes. These technologies can incur additional costs, averaging about $2 million to $10 million for initial implementation and ongoing maintenance. For example, in 2021, Iino Kaiun Kaisha allocated approximately $3 million to enhance its technological capabilities.
Volatile market conditions increase entry risks
The shipping market is susceptible to fluctuations influenced by global economic conditions, trade policies, and environmental factors. For instance, according to the Baltic Dry Index, shipping rates experienced a 75% decline from peak levels in 2021 to the lows seen in 2023. This volatility poses a significant risk for new entrants, who may struggle to maintain profitability during economic downturns.
| Factor | Details | Costs/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Cost of new vessels and infrastructure | $50 million - $100 million |
| Regulatory Compliance | Annual compliance costs | $1 million - $5 million |
| Established Networks | Failure rate of new entrants | 70% |
| Technology Adoption | Initial technology investment | $2 million - $10 million |
| Market Volatility | Baltic Dry Index decline | 75% from peak in 2021 |
Overall, the combination of high capital investment, stringent regulatory requirements, established networks, necessary technology adoption, and volatile market conditions creates a formidable barrier for new entrants in the shipping industry, demonstrating Iino Kaiun Kaisha's strong positioning in this competitive landscape.
The dynamics influencing Iino Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. through Porter's Five Forces illustrate a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges. From the nuanced bargaining power of suppliers and customers to the relentless competitive rivalry, each force plays a pivotal role in shaping the company's strategy. As Iino navigates threats from substitutes and new entrants, understanding these forces will be crucial for sustaining its competitive edge in the ever-evolving shipping industry.
[right_small]Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
