
|
What are the Porter’s Five Forces of Euronav NV (EURN)? |
Fully Editable: Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design: Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Investor-Approved Valuation Models
MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
No Expertise Is Needed; Easy To Follow
Euronav NV (EURN) Bundle
Diving into the world of Euronav NV (EURN) unveils a complex web of interactions shaping its business landscape. Michael Porter’s Five Forces Framework is a vital tool for understanding the dynamics at play, revealing the bargaining power of suppliers and customers, the level of competitive rivalry, the threat of substitutes, and the threat of new entrants. Each force plays a pivotal role in determining Euronav's strategic approach and market positioning. Read on to explore how these elements impact the company’s operations and its standing in the maritime industry.
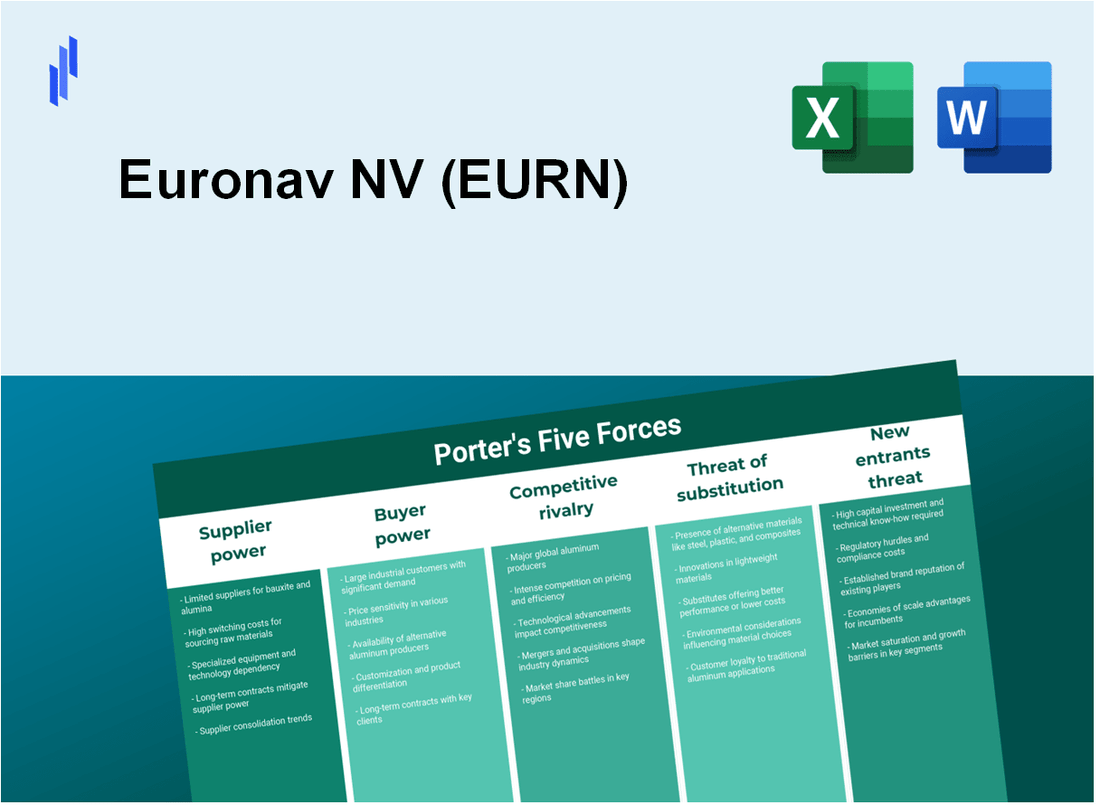
Euronav NV (EURN) - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of suppliers
Limited shipyard options
The shipbuilding industry is characterized by a limited number of specialized shipyards capable of constructing very large crude carriers (VLCCs) and other specific vessels. As of 2023, there are approximately 50 major shipyards globally that can build large, complex vessels. This concentration inherently increases the bargaining power of suppliers.
| Shipyard Location | Shipyards Available | Annual Production Capacity (Ships) | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 12 | 200 | 36% |
| South Korea | 10 | 150 | 30% |
| Japan | 8 | 100 | 18% |
| Europe | 6 | 80 | 14% |
Specialized ship requirements
Euronav's operations require specialized vessels that meet stringent technical specifications for safety and environmental compliance. This specificity means that suppliers of shipbuilding materials and technology can exert greater influence over Euronav due to the bespoke nature of the contracts.
Dependence on crude oil supply
Euronav's business model is heavily reliant on crude oil supply chains. Any fluctuation in crude oil prices can significantly impact shipping rates and operational costs. For instance, the average Brent crude price reached $73 per barrel in 2023, influencing the terms and conditions set by fuel suppliers.
Regulatory compliance costs
Vessels must adhere to a myriad of international regulations, increasing supplier power as companies providing compliant technology and systems, such as scrubbers or ballast water treatment systems, can dictate terms. Compliance investment for Euronav was estimated at over $2 million per ship as of 2023.
| Regulation | Compliance Cost (USD) | Year Implemented | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMO 2020 | $2 million | 2020 | Reduced sulfur emissions |
| Ballast Water Management | $1.5 million | 2017 | Prevent invasive species |
| Marpol Annex VI | $1 million | 2005 | Air pollution prevention |
Shipping fuel price volatility
Fuel costs constitute a significant portion of operating expenses. As of 2023, the cost of low-sulfur fuel oil (LSFO) fluctuated between $550 and $700 per metric ton, affecting Euronav's bargaining position with fuel suppliers.
| Month | Average LSFO Price (USD/MT) |
|---|---|
| January | 650 |
| February | 620 |
| March | 570 |
| April | 600 |
| May | 700 |
Labor union influence
Labor unions hold considerable power in the maritime industry. Approximately 50% of the maritime workforce is unionized, impacting wage negotiations and operational efficiency. Euronav has faced wage demands that can increase operational expenses by up to 15% during negotiations.
- Union Influence: Maritime unions can disrupt operations through strikes or negotiations.
- Wage Increase Example: A 15% increase in labor costs may lead to financial strain if not managed effectively.
- Safety Standards: Labor unions often push for enhanced safety standards, incurring additional costs.
Euronav NV (EURN) - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of customers
High volume shipping contracts
The scale of shipping contracts significantly influences the bargaining power of customers. Major oil companies often engage in high volume shipping contracts to optimize costs. For instance, Euronav's contracts typically range from $30,000 to $50,000 per day for VLCCs (Very Large Crude Carriers). In 2023, Euronav’s total fleet capacity was around 12.5 million dwt (deadweight tonnage), giving clients substantial leverage over pricing based on volume requirements.
Long-term shipping agreements
Long-term shipping agreements create stability but also increase customer bargaining power. Euronav has seen a growth in contracts lasting between 3 to 5 years, providing clients a degree of assurance over shipping rates. With stable long-term agreements, companies like BP and ExxonMobil secure their shipping solutions, leading Euronav to offer competitive pricing structures to maintain client relationships.
Negotiation leverage of major oil companies
Major oil companies hold remarkable negotiation leverage due to their size and purchasing power. In 2022, the top five oil companies (including ExxonMobil, Shell, and BP) controlled approximately 40% of global oil supply. Their massive cargo requirements mean that Euronav must often offer more favorable terms; this can translate to discounts of up to 15-20% off standard shipping rates based on previous contracts.
Availability of alternative shipping companies
The present market features a variety of alternative shipping companies. According to recent statistics, in 2023, there are over 100 companies in the global tanker shipping sector. This level of competition drives prices down and encourages buyers to negotiate hard, as they can easily switch to another provider if Euronav cannot meet their demands, impacting Euronav's pricing strategy and service offerings.
Sensitivity to shipping rates
Customers exhibit a notable sensitivity to shipping rates, particularly in fluctuating oil markets. An analysis of shipping rates indicates that a 10% increase in costs can lead to a 5-7% reduction in cargo volumes ordered by large refineries. In 2023, Euronav reported an average charter rate of $34,000 per day, positioning them in a competitive range; however, any increases could significantly affect their client base.
Demand for timely and safe delivery
Timely and safe delivery remains a non-negotiable factor for buyers in the oil shipping industry. Reports suggest that oil refineries are increasingly demanding compliance with international safety regulations, and delays can lead to substantial financial penalties. In 2023, Euronav achieved an on-time delivery rate of 98%, enabling them to maintain strong relationships with their clients and minimizing the risk of contractual penalties, effectively reinforcing their market position amidst increasing customer demands.
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Average VLCC Charter Rate | $34,000 per day |
| Total Fleet Capacity | 12.5 million dwt |
| Top 5 Oil Companies Market Control | 40% |
| Contract Duration | 3 to 5 years |
| On-time Delivery Rate | 98% |
| Price Sensitivity Impact | 5-7% reduction in volumes for 10% price increase |
Euronav NV (EURN) - Porter's Five Forces: Competitive rivalry
Large number of global competitors
The shipping industry, particularly in the oil transportation sector, is characterized by a large number of global competitors. As of 2023, there are over 800 companies operating in the tanker segment globally. Major players include Teekay, Frontline Ltd., Scorpio Tankers Inc., and Tsakos Energy Navigation Ltd.. Euronav NV ranks among the top 10 largest independent tanker owners.
Price wars among shipping companies
Intense competition has led to frequent price wars among shipping companies. The average daily charter rates for Very Large Crude Carriers (VLCCs) fluctuated significantly in 2022, with rates reaching as high as $40,000 per day during peak demand but dropping to $20,000 per day in periods of oversupply.
Differentiation through fleet size and technology
Euronav operates a fleet of 44 vessels, including 36 VLCCs and 8 Suezmax tankers, totaling a capacity of approximately 11.9 million deadweight tonnage (DWT). This positions Euronav as a significant player in the market. The company invests heavily in new technologies aimed at improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, which can serve as a key differentiator in a competitive landscape.
Customer loyalty and long-term relationships
Establishing customer loyalty is crucial in maintaining a competitive edge. Euronav has long-term contracts with major oil companies, ensuring stable revenue. Approximately 60% of its revenues are derived from contracts with top-tier oil corporations, minimizing the impact of price volatility in the spot market.
Industry consolidation trends
The shipping industry has been witnessing consolidation trends. In 2023, the total number of tanker operators decreased by 15% compared to previous years, indicating a shift towards fewer but larger entities. Euronav itself expanded its market share through strategic mergers and acquisitions, including a merger with Gener8 Maritime in 2018, enhancing its competitive positioning.
Fluctuating global demand for oil transport
The global demand for oil transport has been highly volatile, affecting competitive dynamics. In 2022, global oil demand increased by 5.4 million barrels per day, while projections for 2023 suggest a growth rate of 1.5%. This fluctuation can lead to periods of excess capacity and, consequently, intensified competition among shipping companies.
| Year | Average VLCC Charter Rate ($/day) | Number of Tanker Operators | Euronav Fleet Size (DWT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ~$15,000 | ~950 | ~11.9 million |
| 2022 | $20,000 - $40,000 | ~850 | ~11.9 million |
| 2023 | ~$25,000 | ~800 | ~11.9 million |
Euronav NV (EURN) - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of substitutes
Pipeline transport alternatives
The global pipeline transportation market size was valued at USD 20.27 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 32.94 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.25% from 2021 to 2028. Pipeline transport offers a lower-cost alternative compared to tanker shipping, especially for geographical connections that can be directly served through pipeline infrastructure.
Rail transport options
Rail transport can also serve as an alternative, particularly in regions like North America where rail infrastructure is robust. In 2020, the U.S. freight rail industry generated approximately USD 80 billion in revenue. Rail transport is often considered more environmentally friendly than road transport, which could increase its attractiveness as a substitute in the face of rising fuel prices.
Increasing adoption of renewable energy sources
The global renewable energy market was valued at USD 928 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach USD 1,977 billion by 2025, expanding at a CAGR of 10.4%. As more companies and consumers shift towards renewable energies like wind and solar, the competition against oil-based transport systems intensifies.
Technological advancements in energy storage
The< strong> global energy storage market is projected to grow from USD 9.3 billion in 2020 to USD 24.4 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 17.5%. Emerging technologies in energy storage, such as advanced battery systems, increase the viability of alternatives to crude oil.
Governmental push for green energy solutions
In 2021, the European Union set a target to cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. Governments around the world are investing heavily in green energy initiatives, further putting pressure on traditional oil transport sectors. The U.S. allocated USD 174 billion for clean energy in its infrastructure plan, fostering greater adoption of non-fossil fuel energy sources.
Decreasing dependence on crude oil
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, U.S. crude oil consumption has decreased by 10% from 2019 to 2020. A notable trend in decreasing dependence on crude oil has emerged, with renewable sources accounting for approximately 11% of total U.S. energy consumption in 2020, emphasizing the shift towards alternative forms of energy.
| Alternative Transport Method | Market Size (2020) | Projected Growth (CAGR) | Market Value by 2028/2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Transport | USD 20.27 billion | 6.25% | USD 32.94 billion |
| Rail Transport | USD 80 billion (Revenue) | N/A | N/A |
| Renewable Energy | USD 928 billion | 10.4% | USD 1,977 billion |
| Energy Storage | USD 9.3 billion | 17.5% | USD 24.4 billion |
| Green Energy Investment (U.S.) | N/A | N/A | USD 174 billion |
Euronav NV (EURN) - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of new entrants
High capital investment requirements
The maritime industry, particularly in the crude oil transportation sector, necessitates substantial capital investment. For instance, the cost of a new Very Large Crude Carrier (VLCC) can reach approximately $100 million to $130 million. This significant financial barrier limits the number of potential new entrants.
Regulatory and compliance hurdles
New entrants in the maritime industry face stringent regulatory requirements, including compliance with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) standards and the International Safety Management (ISM) Code. Compliance costs can range widely, often reaching several millions annually, depending on the size and scope of operations.
Established relationships with major oil customers
Euronav has developed long-standing relationships with major oil corporations, such as BP, Shell, and ExxonMobil. These relationships have been pivotal in securing contract agreements. For example, Euronav had approximately 39% of its revenues derived from long-term contracts as of 2022, illustrating the competitive edge established businesses have over new entrants.
Economies of scale advantages
Large shipping firms like Euronav benefit from economies of scale, enabling them to reduce per-unit costs significantly as they grow. In 2023, Euronav's fleet consisted of approximately 43 vessels, allowing it to spread fixed costs over a larger operational base. This scale disadvantage can deter new entrants who cannot match such fleet sizes and operational efficiencies.
Experience and expertise in maritime operations
The maritime industry requires specific knowledge and operational expertise. Euronav, founded in 2003, has accumulated over 20 years of experience in tanker operations, safety management, and logistics which creates a significant knowledge barrier for new entrants who have yet to develop such expertise.
Access to financing and insurance in the maritime industry
New entrants generally struggle to secure financing due to the high-risk nature of the maritime sector. Euronav has established relationships with financial institutions and underwriters that support its operations. The average cost of insuring a VLCC can range from $50,000 to $80,000 annually, depending on various factors, including the vessel's value and operational history. New entrants may not have the same access to favorable terms, making it challenging to obtain the necessary insurance and financing.
| Factor | Details | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | VLCC cost range: $100M - $130M | High entry barrier |
| Regulatory Compliance | Annual compliance costs: several millions | Increases operational costs |
| Established Relationships | 39% revenue from long-term contracts | Difficulties in securing contracts |
| Economies of Scale | Fleet size: 43 vessels | Lower per-unit costs |
| Experience | Over 20 years in operation | Knowledge barrier for new firms |
| Access to Financing | VLCC insurance cost: $50K - $80K annually | Financing challenges for newcomers |
In examining the intricate landscape of Euronav NV's (EURN) business through the lens of Michael Porter’s Five Forces Framework, it's evident that the company navigates a challenging environment shaped by strong supplier and customer dynamics, amidst fierce competition. The threats posed by substitutes and potential new entrants loom within a context marked by high capital requirements and fluctuating market conditions. Ultimately, an astute understanding of these factors will be crucial for Euronav as it endeavors to maintain its position and leverage opportunities within the volatile shipping industry.
[right_ad_blog]Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
