
|
United States Cellular Corporat (UZE): Porter's 5 Forces Analysis |
Fully Editable: Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design: Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Investor-Approved Valuation Models
MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
No Expertise Is Needed; Easy To Follow
United States Cellular Corporat (UZE) Bundle
In the dynamic world of telecommunications, understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for navigating challenges and seizing opportunities. United States Cellular Corporation operates in an environment shaped by Michael Porter’s Five Forces, a framework that sheds light on supplier and customer bargaining power, competitive rivalry, the threat of substitutes, and the potential for new entrants. Delve deeper as we explore these forces and uncover the strategic implications for US Cellular in today's fast-evolving market.
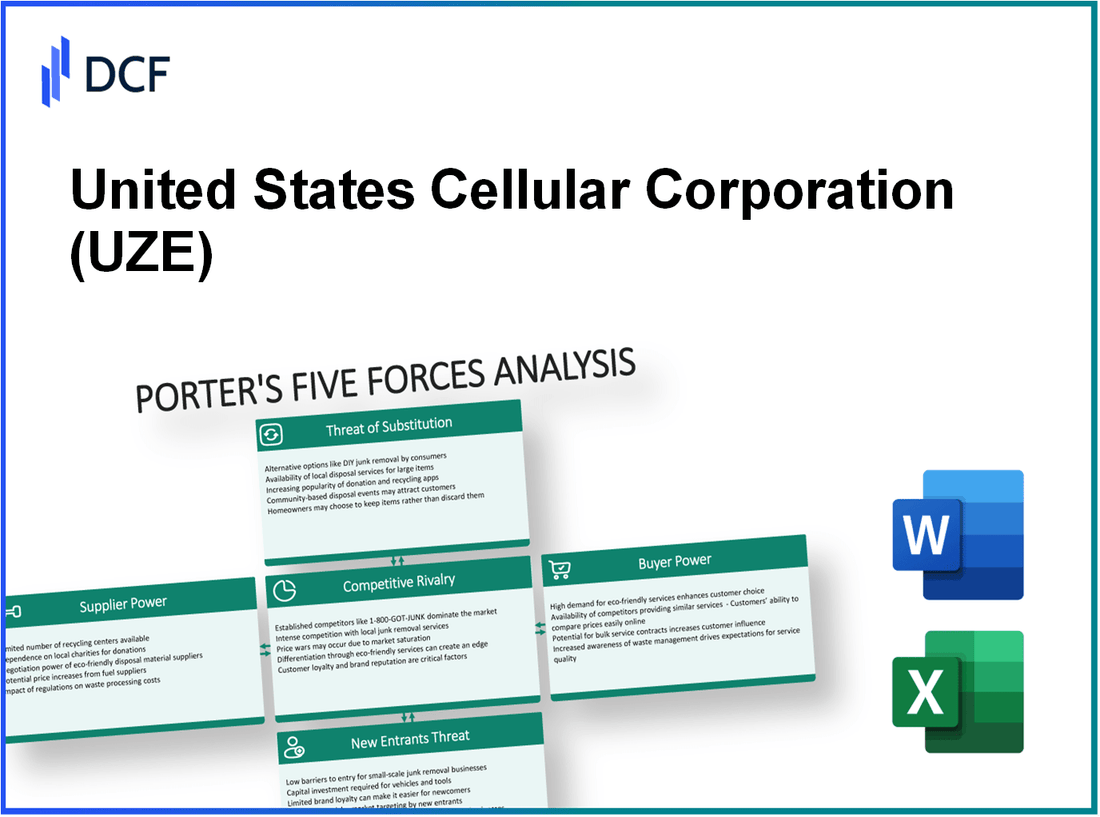
United States Cellular Corporat - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in the telecommunications industry is influenced by several key factors that impact United States Cellular Corporation's operational costs and strategic planning.
Limited number of network equipment providers
The telecommunications sector relies heavily on a limited number of network equipment providers. In the U.S., companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, and Cisco command substantial market shares. For example, as of 2023, Ericsson and Nokia together control approximately 40% of the global telecom equipment market, which constrains U.S. Cellular's options for sourcing equipment.
High cost of switching suppliers
Switching suppliers in this industry incurs significant costs, including potential downtime and the need to retrain staff on new equipment. According to a report from Deloitte, the average cost of switching telecommunications equipment suppliers can exceed $10 million. This high switching cost creates a dependency on existing suppliers, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Essential component suppliers hold leverage
Essential components, such as chipsets and software, are often sourced from specialized suppliers. For instance, Qualcomm, which supplies about 30% of smartphone chipsets, holds substantial leverage in negotiations due to the critical nature of their products for mobile networks. This reliance allows suppliers to implement price increases without fearing a loss of business.
Potential long-term contracts reduce power
United States Cellular often enters into long-term contracts with its suppliers, which mitigates supplier power by locking in prices for extended periods. For example, agreements extending up to 5 years help stabilize costs against volatility in supplier pricing. However, during contract renewals, suppliers may negotiate higher prices, impacting U.S. Cellular's overall expenditure.
Suppliers' ability to forward integrate
Some suppliers possess the ability to forward integrate, potentially entering the telecommunications market themselves. For example, companies like Amazon and Google have considered expanding into telecom services, which could disrupt traditional supplier-buyer dynamics. This potential shift adds a layer of risk for U.S. Cellular as they navigate supplier relationships.
| Factor | Details | Impact on U.S. Cellular |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Network Equipment Providers | Major players include Ericsson, Nokia, and Cisco | Increased dependency on few suppliers |
| High Switching Costs | Averaging over $10 million | Inhibits changing suppliers, raises costs |
| Leverage of Essential Components | Qualcomm supplies about 30% of chipsets | Potential for price increases, impacting margins |
| Long-Term Contracts | Contracts extending up to 5 years | Stabilizes costs but risk during renewals |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential market entry by suppliers like Amazon | Increases competitive pressure on U.S. Cellular |
United States Cellular Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Bargaining power of customers
The wireless services market is characterized by a multitude of options for consumers. As of Q3 2023, there are over 1,500 wireless service providers operating in the United States, contributing to significant buyer power.
Consumers exhibit a high level of price sensitivity. A survey conducted by the Federal Communications Commission in 2022 indicated that approximately 63% of respondents considered cost the primary factor when selecting a wireless provider. This sensitivity pressures companies to offer competitive pricing to retain and attract customers.
Low switching costs enhance the bargaining power of customers. With no substantial fees or penalties attached to changing providers, customers can easily switch their service. A report from Consumer Reports stated in 2023 that 40% of wireless customers have switched providers in the past year, demonstrating the ease with which consumers can make changes.
The demand for data-driven services is escalating. According to Statista, mobile data traffic in the U.S. is projected to reach 21.6 exabytes per month by 2026, up from 10.1 exabytes in 2022. This increasing reliance on data services compels providers like United States Cellular Corporation to tailor their offerings, thereby amplifying customer power.
Moreover, customer service and brand reputation significantly influence consumer behavior. J.D. Power’s 2022 U.S. Wireless Customer Care Study found that companies with higher customer satisfaction ratings, such as those providing excellent support, experience 20% less churn compared to their competitors. United States Cellular Corporation's customer service rating was 809 out of 1,000, which is above the industry average of 798.
| Bargaining Power Factors | Current Impact Level | Statistical Data |
|---|---|---|
| Numerous alternatives for wireless services | High | Over 1,500 providers in the U.S. |
| Price sensitivity among consumers | High | 63% cite cost as a primary factor |
| Low switching costs for customers | High | 40% switched providers in the past year |
| Increasing demand for data-driven services | High | Projected 21.6 exabytes per month by 2026 |
| Influence of customer service and brand reputation | Medium | Customer service rating of 809 out of 1000 |
United States Cellular Corporat - Porter's Five Forces: Competitive rivalry
The competitive landscape for United States Cellular Corporation (USCC) is marked by several factors that shape its market position and strategy. The presence of large national carriers is a significant element in this rivalry.
Presence of large national carriers
USCC faces stiff competition from major players such as Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile. As of Q2 2023, Verizon holds approximately 30% market share, AT&T has around 29%, and T-Mobile commands about 26% of the U.S. wireless market.
Intense price competition and promotional activities
Price competition is fierce, with multiple carriers offering unlimited plans starting at $70 per month. USCC has had to engage in promotional campaigns to retain customers. For example, its recent offer included a $700 credit for customers switching from competitors. Such promotions are designed to mitigate churn rates averaging around 1.1% for USCC in 2023.
High advertising expenditure to maintain market share
To compete effectively, USCC has increased its advertising budget significantly. In 2022, the company spent approximately $300 million on marketing and promotions, representing an increase of 10% from the previous year. This expenditure is critical in a market where T-Mobile spent about $1.5 billion on advertising in the same period.
Competitive advancements in technology and offerings
Technological advancements are crucial in maintaining a competitive edge. In 2023, USCC announced an investment of $1 billion to enhance its network infrastructure. This includes expanding its LTE and introducing 5G services, which are vital for keeping pace with industry leaders like Verizon, which has already rolled out its nationwide 5G network to over 230 million people as of mid-2023.
Growing importance of 5G network expansion
The shift to 5G is transforming the competitive landscape. Major competitors are investing heavily in this area. For instance, AT&T plans to spend a total of $24 billion on 5G infrastructure by 2025, while T-Mobile is focusing on expanding its 5G coverage to reach 300 million people by year-end 2023. USCC aims to increase its 5G footprint and has allocated $500 million specifically for 5G development in 2023.
| Carrier | Market Share (%) | 2023 Advertising Expenditure ($ million) | 5G Coverage Target Population (million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verizon | 30 | 1,500 | 230 |
| AT&T | 29 | 1,300 | 300 |
| T-Mobile | 26 | 1,500 | 300 |
| United States Cellular Corporation | 4 | 300 | Targeting 10 million by 2025 |
As of 2023, USCC's competitive strategy revolves around these key factors, each influencing its market dynamics and growth prospects in a highly competitive environment.
United States Cellular Corporation - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes for United States Cellular Corporation (US Cellular) has become increasingly pronounced in recent years, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences.
Increasing use of internet-based communication apps
As of 2023, approximately 3.9 billion people globally use messaging apps, with platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Telegram dominating the market. This represents a growth rate of 10% year-over-year, indicating a substantial shift towards Internet-based communication modalities over traditional cellular services. In the U.S. alone, over 80% of smartphone users have downloaded at least one messaging app, further demonstrating this trend.
Emergence of Wi-Fi and VoIP services
Wi-Fi services have become a viable alternative for voice and data communication. According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) report in 2022, around 90% of U.S. homes are equipped with Wi-Fi, which supports various voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services. VoIP adoption has surged, with the number of users reaching approximately 80 million in the U.S. by the end of 2022, highlighting a significant shift away from traditional voice services.
Potential for satellite communications as an alternative
Satellite communication technology is evolving rapidly, with companies such as Starlink leading the charge. As of mid-2023, Starlink claims to have over 1 million active subscribers globally, offering broadband services that compete directly with traditional cellular networks. The company has announced plans to expand its services in rural areas, which could directly impact US Cellular’s customer base, particularly in less densely populated regions.
Lower cost options for communication
Price sensitivity is a significant factor influencing the threat of substitutes. Prepaid mobile plans and budget carriers have gained popularity, with plans averaging around $25 per month. In contrast, US Cellular's average customer revenue per user (ARPU) stood at $42.50 as of the second quarter of 2023. This discrepancy presents a threat as consumers seek more economical alternatives.
Bundled service offerings from competitors
Major competitors such as Verizon and AT&T have leveraged bundled service offerings, including internet, television, and mobile service packages. Verizon's “5G Home Internet” and AT&T's “AT&T Fiber” packages cater to a growing segment of consumers looking for all-in-one solutions. A recent industry report indicated that bundling can reduce churn rates by approximately 30%, posing a challenge to US Cellular in retaining customers.
| Service Type | Average Monthly Cost | Number of Users (2023) | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| US Cellular | $42.50 | 4.8 million | 3.5 |
| Wi-Fi & VoIP Services | $30.00 | 80 million | 58.8 |
| Starlink | $110.00 | 1 million | 0.7 |
| Prepaid Carriers | $25.00 | 30 million | 21.8 |
| Bundled Services (Verizon/AT&T) | $100.00 | 40 million | 29.2 |
United States Cellular Corporat - Porter's Five Forces: Threat of new entrants
The telecommunications industry presents significant challenges for new entrants, particularly for companies like United States Cellular Corporation (US Cellular). The following factors contribute to the analysis of the threat of new entrants in this sector.
High capital investments required for infrastructure
Establishing a telecommunications network demands substantial capital investment. For instance, building a single cell tower can cost between $100,000 and $500,000 depending on location and technology. US Cellular has a capital expenditure of approximately $650 million for network infrastructure improvements in 2022 alone. This high barrier makes it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively.
Regulatory barriers and spectrum licensing challenges
The telecommunications market is heavily regulated, with licensing requirements creating further obstacles. For example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) auctioned off 5G spectrum licenses in 2020, raising a total of $81 billion in bids. New companies entering the market must navigate this complex licensing landscape, which can take years and significant financial resources.
Established brand loyalty towards existing players
Brand loyalty is another critical barrier for new entrants. US Cellular reported that it has approximately 4.9 million subscribers, supported by strong customer satisfaction scores. According to J.D. Power, US Cellular ranks within the top tier for customer service in the regional carrier category. Such loyalty can be challenging for newcomers to overcome.
Economies of scale advantage for current leaders
Existing players like US Cellular benefit from economies of scale that lower their average costs. For example, in 2022, US Cellular's average revenue per user (ARPU) was around $43, while larger competitors achieved significantly lower operational costs. This scale allows established companies to offer competitive pricing, further discouraging potential new entrants.
Rapid technological advancements necessary for competitiveness
The telecommunications landscape is characterized by rapid technological change. Companies are investing heavily in new technologies; for instance, in the race for 5G deployment, US Cellular allocated a portion of its capital expenditures towards this initiative, with estimates of around $300 million in network upgrades. New entrants may find it difficult to keep pace with such investments.
| Factor | Details | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Cost of building a cell tower | $100,000 - $500,000 |
| Regulatory Barriers | FCC spectrum auction revenue in 2020 | $81 billion |
| Brand Loyalty | Total subscribers for US Cellular | 4.9 million |
| Economies of Scale | Average revenue per user (ARPU) | $43 |
| Technology Investment | Estimated capital for network upgrades | $300 million |
In analyzing United States Cellular Corporation through Porter's Five Forces, it becomes clear that the telecommunications landscape is complex, with significant pressure from suppliers and customers alike, fierce competition from established carriers, and notable substitutes challenging traditional services. While the threat of new entrants remains a concern due to substantial barriers to entry, understanding these dynamics is essential for strategic positioning and long-term success in a rapidly evolving market.
[right_small]Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
