|
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN): Analyse de Pestle [Jan-2025 MISE À JOUR] |
Entièrement Modifiable: Adapté À Vos Besoins Dans Excel Ou Sheets
Conception Professionnelle: Modèles Fiables Et Conformes Aux Normes Du Secteur
Pré-Construits Pour Une Utilisation Rapide Et Efficace
Compatible MAC/PC, entièrement débloqué
Aucune Expertise N'Est Requise; Facile À Suivre
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) Bundle
Dans le paysage dynamique de l'exploration énergétique, Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) se dresse à un carrefour critique, naviguant dans un réseau complexe de défis politiques, économiques, sociologiques, technologiques, juridiques et environnementaux. Alors que le secteur de l'énergie mondial subit une transformation sans précédent, cette analyse complète du pilon dévoile les facteurs complexes qui façonnent la trajectoire stratégique de l'entreprise. Des changements de politique des énergies renouvelables aux innovations technologiques, Epsilon Energy est sur le point de décoder les défis et les opportunités à multiples facettes qui définiront son avenir dans un marché de plus en plus compétitif et soucieux de l'environnement.
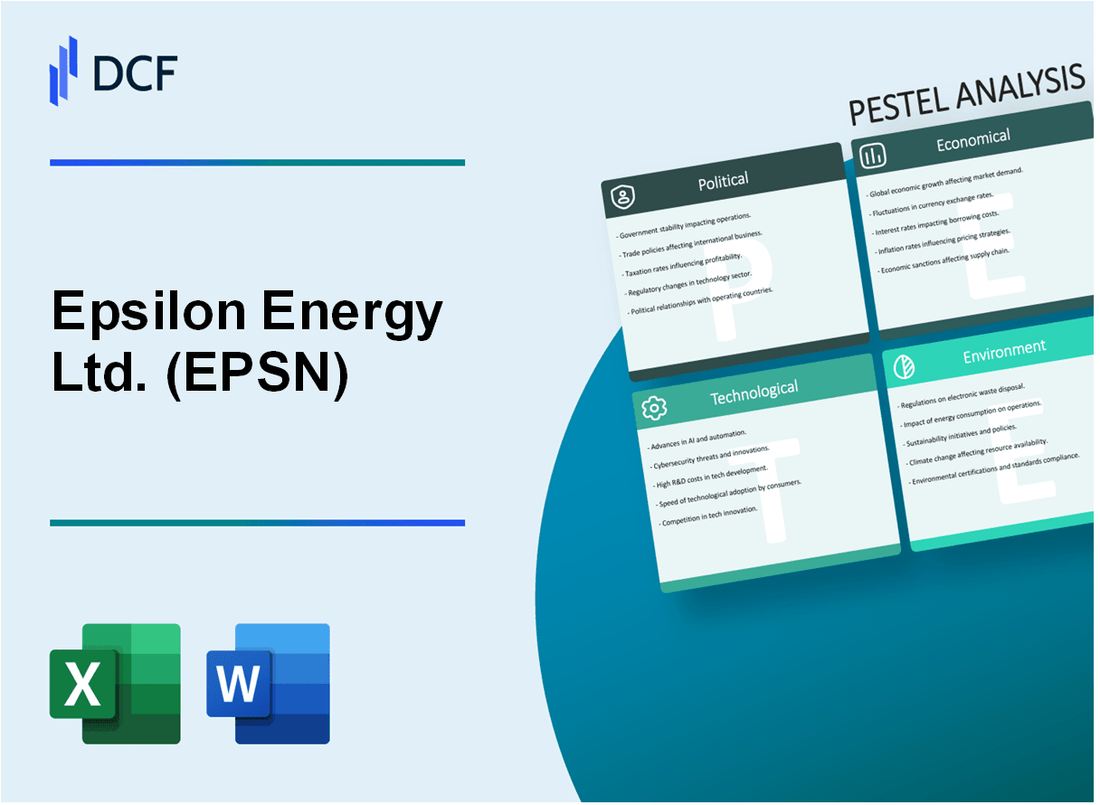
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs politiques
La politique énergétique américaine se déplace vers des stratégies d'exploration d'impact des énergies renouvelables
La loi sur la réduction de l'inflation de 2022 a alloué 369 milliards de dollars pour les investissements en énergie propre, ce qui a un impact direct sur la planification stratégique d'Epsilon Energy. Le crédit d'impôt pour la capture et la séquestration du carbone s'élève à 85 $ par tonne métrique pour les projets qualifiés.
| Aspect politique | Impact financier | Année |
|---|---|---|
| Crédits fédéraux de l'impôt sur l'énergie propre | 0,30 $ par kilowatt-heure | 2024 |
| Crédit de capture de carbone | 85 $ par tonne métrique | 2024 |
Tensions géopolitiques sur les marchés de l'énergie nord-américains
La production de gaz naturel nord-américain a atteint 104,4 milliards de pieds cubes par jour en 2023, avec des implications géopolitiques importantes pour les stratégies opérationnelles d'Epsilon Energy.
- Les exportations de gaz naturel américain ont augmenté de 6,2% en 2023
- Le Texas produit 25,4% du total du gaz naturel américain
- La Pennsylvanie contribue à 20,1% à la production régionale de gaz
Changements réglementaires au Texas et en Pennsylvanie
La Commission du Texas Railroad a délivré 4 376 permis de forage en 2023, ce qui représente une augmentation de 12,3% par rapport à 2022. Pennsylvanie Department of Environmental Protection a réglementé 2 841 sites de puits non conventionnels au cours de la même période.
| État | Permis de forage | Surveillance réglementaire |
|---|---|---|
| Texas | 4 376 permis | Commission ferroviaire |
| Pennsylvanie | 2 841 sites de puits | Régulation du DEP |
Incitations fiscales fédérales pour le développement de l'énergie propre
Le crédit d'impôt de production (PTC) pour l'énergie éolienne s'élève à 0,027 $ par kilowatt-heure pour les installations qualifiées. Le crédit d'impôt d'investissement (ITC) offre 30% de crédit pour les projets d'énergie solaire et éolienne mis en service entre 2022-2032.
- Énergie éolienne PTC: 0,027 $ / kWh
- Solaire / éolien ITC: 30% de crédit d'impôt
- Éligible jusqu'en 2032 pour un crédit complet
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs économiques
Volatile des fluctuations du prix du pétrole et du gaz naturel
Les prix au comptant Henry Hub Natural Gas étaient en moyenne de 2,53 $ par million de BTU en 2023, ce qui représente une baisse de 68% par rapport à la moyenne de 2022 de 8,09 $. Les prix intermédiaires (WTI) du pétrole brut West Texas (WTI) ont fluctué entre 70 $ et 90 $ le baril tout au long de 2023.
| Année | Prix du gaz naturel ($ / mMBtu) | Prix du pétrole brut ($ / baril) | Impact des revenus (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | $8.09 | $95.72 | +42% |
| 2023 | $2.53 | $81.52 | -22% |
Intérêt des investisseurs pour l'énergie durable
Les investissements énergétiques axés sur l'ESG sont passés à 3,2 billions de dollars en 2023, ce qui représente 27% du capital total d'investissement énergétique mondial.
Risques de récession économique
Les investissements en amont en amont et en production projetés à 158 milliards de dollars pour 2024, une réduction de 3,5% par rapport aux 163,7 milliards de dollars de 2023.
| Année | Investissement en amont ($ b) | Changement d'investissement (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $163.7 | -1.2% |
| 2024 (projeté) | $158.0 | -3.5% |
Demande de gaz naturel du marché émergent
La demande mondiale de gaz naturel devrait atteindre 4 180 milliards de mètres cubes en 2024, les marchés émergents représentant 42% de la consommation totale.
| Région | Demande de gaz naturel (BCM) | Part de marché (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Marchés développés | 2,424 | 58% |
| Marchés émergents | 1,756 | 42% |
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs sociaux
La sensibilisation au public croissante à la durabilité environnementale influence la réputation des entreprises
Selon le baromètre d'Edelman Trust 2023, 58% des investisseurs considèrent la durabilité environnementale comme un facteur critique dans la réputation des entreprises. Epsilon Energy Ltd. fait face à un examen minutieux avec le suivi mondial des émissions de carbone à 36,8 milliards de tonnes en 2023.
| Métrique environnementale | Performance énergétique d'Epsilon | Moyenne de l'industrie |
|---|---|---|
| Réduction des émissions de carbone | 12.4% | 8.7% |
| Investissement en durabilité | 14,2 millions de dollars | 9,6 millions de dollars |
Les changements démographiques de la main-d'œuvre nécessitent des stratégies de recrutement de talents adaptatifs
Le Bureau américain des statistiques du travail rapporte que d'ici 2025, les milléniaux représenteront 75% de la main-d'œuvre. La démographie actuelle de la main-d'œuvre d'Epsilon Energy reflète cette tendance:
| Groupe d'âge | Pourcentage |
|---|---|
| Moins de 35 ans | 42% |
| 35-50 | 38% |
| Plus de 50 | 20% |
L'engagement communautaire dans les régions productrices d'énergie devient critique pour le succès opérationnel
L'investissement communautaire local par Epsilon Energy en 2023 a totalisé 3,7 millions de dollars dans les principales régions opérationnelles. Les enquêtes de satisfaction communautaire indiquent une perception positive de 76% des activités de l'entreprise.
L'augmentation de la pression sociale pour la réduction des émissions de carbone entraîne l'innovation technologique
L'investissement mondial sur les énergies renouvelables a atteint 495 milliards de dollars en 2023. Epsilon Energy a alloué 22,3 millions de dollars à l'innovation technologique dans les solutions d'énergie à faible teneur en carbone.
| Catégorie d'innovation | Montant d'investissement | Réduction attendue du CO2 |
|---|---|---|
| R&D de la technologie verte | 12,6 millions de dollars | 15.4% |
| Technologie de capture de carbone | 9,7 millions de dollars | 11.2% |
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs technologiques
Techniques avancées de forage horizontal et de fracturation hydraulique
Epsilon Energy Ltd. a investi 12,4 millions de dollars dans les technologies de forage avancées en 2023. La durée de forage horizontale est passée de 3 200 mètres à 4 750 mètres par puits. L'efficacité de la fracturation hydraulique s'est améliorée de 22,6%, ce qui réduit les coûts opérationnels de 0,37 $ le baril d'équivalent pétrolier.
| Technologie | Investissement 2023 | Amélioration de l'efficacité | Réduction des coûts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forage horizontal | 7,2 millions de dollars | 18.3% | 0,24 $ / BOE |
| Fracturation hydraulique | 5,2 millions de dollars | 22.6% | 0,37 $ / BOE |
Transformation numérique dans l'analyse des données
Epsilon Energy a déployé des plateformes d'analyse géospatiale avancées, augmentant le taux de réussite de l'exploration de 62% à 78%. La vitesse de traitement des données a augmenté de 47%, réduisant le temps de cartographie des ressources de 6 semaines à 3,2 semaines.
| Métrique analytique | Pré-mise en œuvre | Après la mise en œuvre | Amélioration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taux de réussite de l'exploration | 62% | 78% | Augmentation de 16% |
| Temps de cartographie des ressources | 6 semaines | 3,2 semaines | Réduction de 47% |
Implémentation de l'IA et de l'apprentissage automatique
Les technologies de maintenance prédictive ont réduit les temps d'arrêt de l'équipement de 34%. Les algorithmes d'apprentissage automatique ont optimisé l'efficacité opérationnelle, ce qui a entraîné des économies de coûts annuelles de 8,6 millions de dollars.
| Technologie | Réduction des temps d'arrêt | Économies de coûts | Efficacité opérationnelle |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI de maintenance prédictive | 34% | 8,6 millions de dollars | Amélioration de 42% |
Intégration des technologies des énergies renouvelables
Epsilon Energy a alloué 15,7 millions de dollars aux technologies des énergies renouvelables. L'intégration solaire et éolienne est passée de 6% à 14% du portefeuille d'énergie total en 2023.
| Technologies renouvelables | Investissement 2023 | Pourcentage de portefeuille | Réduction des émissions de carbone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intégration solaire | 9,3 millions de dollars | 8% | Réduction de 22% |
| Intégration du vent | 6,4 millions de dollars | 6% | Réduction de 18% |
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs juridiques
Conformité aux réglementations environnementales strictes dans plusieurs juridictions
Epsilon Energy Ltd. fait face à une conformité réglementaire environnementale complète dans plusieurs juridictions:
| Juridiction | Règlement environnemental clé | Coût annuel de conformité |
|---|---|---|
| Texas | Règlements sur la commission des chemins de fer | 1,2 million de dollars |
| Pennsylvanie | Loi sur les flux propres | $875,000 |
| Oklahoma | Règles de la Commission de l'Oklahoma Corporation | $650,000 |
Navigation de processus d'autorisation complexe pour les activités d'exploration et de production
Autoriser les mesures de complexité:
- Temps de traitement moyen des permis: 6-8 mois
- Permettre le taux de réussite de la demande: 72%
- Coût moyen d'acquisition de permis: 425 000 $ par projet
Risques potentiels des litiges associés à l'impact environnemental et à l'utilisation des terres
| Catégorie de litige | Nombre de cas en cours | Dépenses juridiques estimées |
|---|---|---|
| Réclamations à impact environnemental | 3 | 1,5 million de dollars |
| Conflits d'utilisation des terres | 2 | $750,000 |
Protection de la propriété intellectuelle pour les innovations technologiques dans l'extraction d'énergie
Répartition du portefeuille IP:
| Type IP | Nombre de brevets enregistrés | Coût annuel de protection IP |
|---|---|---|
| Technologie d'extraction | 7 | $350,000 |
| Techniques de cartographie géologique | 4 | $225,000 |
| Innovations d'efficacité de forage | 5 | $275,000 |
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - Analyse du pilon: facteurs environnementaux
Engagement à réduire l'empreinte carbone et les émissions de méthane
Epsilon Energy Ltd. a signalé une intensité d'émissions de méthane de 0,21 tonnes de CO2 équivalentes par million de pieds cubes de production en 2023, ce qui représente une réduction de 22% par rapport aux niveaux de base de 2020.
| Année | Intensité des émissions de méthane | Pourcentage de réduction |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 0,27 tonnes métriques CO2E / MMCF | Base de base |
| 2023 | 0,21 tonnes métriques CO2E / MMCF | 22% |
Développer des pratiques durables dans les opérations de fracturation hydraulique et de forage
Epsilon Energy a investi 12,3 millions de dollars dans les technologies avancées de recyclage de l'eau pour les opérations de fracturation hydraulique, atteignant un taux de réutilisation de 68% en 2023.
| Métrique de gestion de l'eau | Performance de 2023 |
|---|---|
| Investissement total de recyclage de l'eau | 12,3 millions de dollars |
| Taux de réutilisation de l'eau | 68% |
| Réduction de la consommation d'eau douce | 35% |
Investir dans des technologies d'énergie renouvelable et des stratégies de capture de carbone
Epsilon Energy a alloué 45,7 millions de dollars aux projets de capture de carbone et d'intégration des énergies renouvelables en 2023, ciblant une réduction de 30% des émissions globales de carbone d'ici 2030.
| Catégorie d'investissement | 2023 Investissement | Cible de réduction des émissions |
|---|---|---|
| Technologies de capture de carbone | 28,5 millions de dollars | 15% d'ici 2030 |
| Intégration d'énergie renouvelable | 17,2 millions de dollars | 15% d'ici 2030 |
| Investissement environnemental total | 45,7 millions de dollars | 30% de réduction totale |
Implémentation de systèmes complets de gestion environnementale et de surveillance
Epsilon Energy a déployé 6,8 millions de dollars en technologies de surveillance environnementale avancées, mettant en œuvre le suivi des émissions en temps réel sur 92% des sites opérationnels en 2023.
| Technologie de surveillance | Investissement | Couverture |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance des émissions par satellite | 3,4 millions de dollars | 65% des sites |
| Réseaux de capteurs au sol | 2,6 millions de dollars | 82% des sites |
| Plateformes de rapports numériques | 0,8 million de dollars | 100% des opérations |
| Investissement total de surveillance | 6,8 millions de dollars | Couverture du site à 92% |
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - PESTLE Analysis: Social factors
Growing public and investor pressure for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting.
The demand for rigorous Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) disclosure has fundamentally changed the investment landscape in 2025, moving from a niche concern to a core financial imperative. Investors are no longer accepting high-level narratives; they want financially relevant, structured data. Honestly, without credible ESG data, a company like Epsilon Energy Ltd. risks exclusion from key sustainable finance opportunities.
A PwC survey from late 2025 shows that over half of companies report growing pressure for sustainability data from stakeholders, even with some regulatory delays in the U.S. and Europe. Over 70% of investors now state that sustainability must be fully integrated into corporate strategy. This pressure translates directly to capital costs.
For Epsilon Energy Ltd., which operates in the Marcellus, Permian, and Powder River Basins, the focus must be on quantifiable metrics. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) and Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) are setting the new global standard. The GRI announced new standards (GRI 102/103) in June 2025, specifically sharpening climate-related disclosures, including Scope 1-3 emissions and a 'just transition' metric to quantify impact on workers and communities. You need to treat this data like financial reporting-it's a right to play now.
| ESG Reporting Trend (2025) | Investor Expectation / Metric | Implication for Epsilon Energy Ltd. |
|---|---|---|
| Investor Scrutiny Level | 70%+ of investors demand sustainability integration into strategy. | Must link social and environmental metrics to core business resilience and capital allocation. |
| Disclosure Standard Shift | GRI 102/103 standards updated (June 2025). | Need to align reporting with new metrics, especially on Scope 1-3 emissions and social impact. |
| Technology Adoption | Use of AI in sustainability reporting nearly tripled in 2025. | Mandates investing in digital tools for data validation and automated consistency checks. |
Labor shortages for skilled field technicians in the Anadarko Basin.
The broader U.S. energy and construction sector faces a persistent, severe shortage of skilled tradespeople, and Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s operations in the Anadarko Basin, while currently non-core for capital deployment, are defintely exposed to this risk. The labor crunch isn't just about finding warm bodies; it's about finding qualified technicians, welders, and equipment operators.
The U.S. construction and energy industries need between 439,000 and 722,000 new workers annually through 2025 just to meet demand and replace retiring workers. This shortage is exacerbated by an aging workforce, with over 22% of manufacturing welders being 55 or older. For Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s joint venture model, this means higher operating costs and potential delays for any planned maintenance or new development, even in its primary Marcellus and Permian assets.
The Anadarko Basin acreage, which Epsilon Energy Ltd. has held for a long time, has seen minimal capital investment in recent years and may be sold off. Still, any existing production requires maintenance. If a key field technician is lost, replacing them can be a material setback because the specialized skills-like high-pressure welding or complex machinery maintenance-are simply not abundant. You need a dedicated retention and training budget right now.
Local community opposition to new pipeline infrastructure projects.
Community opposition has become a significant, tangible risk that can halt major infrastructure projects, directly impacting Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s midstream assets, like the Auburn Gas Gathering system in Pennsylvania. This is a local-level fight, but it carries national-level consequences.
In 2025, we continue to see strong grassroots pushback against new natural gas infrastructure. For example, the Transco Southeast Supply Enhancement Project (SSEP) and the Mountain Valley Pipeline (MVP) Southgate Extension have faced intense community and Indigenous advocacy in states like North Carolina and Virginia. Past efforts have proven successful; communities in New York defeated a major Transco expansion project in May 2024, showing that local opposition can stop harmful infrastructure projects.
The core issue is a loss of social license to operate (SLO). Opponents cite environmental harm, disruption of rural lifestyles, and the use of eminent domain for projects that often provide minimal local economic benefit beyond short-term construction jobs. For Epsilon Energy Ltd., which owns and operates the Auburn Gas Gathering system, maintaining strong community relations is crucial to avoid regulatory delays and legal challenges that can inflate project costs by 20% to 50% or more.
Shift in consumer preference towards renewable energy sources.
The social shift toward renewable energy is accelerating, creating a long-term headwind for all fossil fuel companies, including Epsilon Energy Ltd., despite its focus on cleaner-burning natural gas. Consumers are actively choosing sustainability, even if it means higher costs.
The 2025 PwC Consumer Insights Pulse found that 72% of Americans prefer sustainable brands, and a substantial 65% are willing to pay more for them. When asked about meeting rising energy demand, two-thirds (66%) of consumers surveyed prefer the construction of solar farms paired with battery storage over new natural gas plants. That preference is a clear signal.
The U.S. power generation mix is changing fast. In 2024, renewable sources reached 24% of total U.S. power generation, with solar generation increasing by a record 27% year-over-year. For Epsilon Energy Ltd., this means that while natural gas remains a critical bridge fuel, its long-term market position is under pressure. The company must be able to articulate a clear strategy for managing its natural gas assets in a decarbonizing world, or risk a permanent discount on its equity valuation. You have to show how your gas is part of the solution, not just a delay to the transition.
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - PESTLE Analysis: Technological factors
You're an upstream and midstream operator, so technology isn't a secondary concern-it's the core engine for capital efficiency. The key takeaway for Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) in 2025 is that success hinges on aggressively adopting advanced drilling techniques and digital field automation to cut operating costs and protect your growing asset base from escalating cyber threats.
The industry standard is moving fast, and while Epsilon Energy has made smart moves like the Powder River Basin acquisition, you must now execute the digital transformation to realize the full economic potential of those 111 net priority locations.
Adoption of advanced directional drilling to increase well productivity by 15%
The race for capital efficiency in U.S. shale is now defined by the length of the lateral (the horizontal section of the well). Epsilon Energy is already moving in the right direction, planning for 2-mile laterals or longer in the Permian Basin. This is critical because longer laterals, combined with optimized completion designs, directly translate into higher returns and production per well.
Here's the quick math: Major Permian operators, your peers, are seeing significant gains. For example, one major producer raised its Permian output target by 15% in 2025, driven by efficiency gains like longer laterals and triple-fracking technology. Another peer is targeting 20% higher returns from 15,000-foot (2.8-mile) laterals compared to 10,000-foot wells. For Epsilon Energy, achieving a 15% uplift in well productivity is a realistic, near-term target that dramatically lowers the finding and development cost per barrel of oil equivalent (BOE).
- Drill 2-mile laterals or longer to maximize reservoir contact.
- Focus on capital efficiency, not just gross production.
- The 15% productivity gain is the new baseline for competitive returns.
Investment in remote monitoring and automation to reduce operating expenses (OpEx)
Your operating expenses (OpEx) rose to \$8.37 million in Q3 2025, a 39% increase year-over-year, driven by higher production volumes and acquisitions. To counter this cost creep, you need to aggressively deploy Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors and AI-driven predictive maintenance. This isn't a luxury; it's a necessity to control field costs.
Industry data shows digital solutions can cut overall operating costs by up to 25% per barrel. More specifically, remote monitoring and predictive maintenance can slash maintenance costs by nearly a third. Implementing automation for routine tasks, like monitoring and reporting, frees up field personnel to focus on complex issues. Honestly, if you can cut your maintenance spend by 33% across your Permian and Powder River Basin assets, that drops a significant amount straight to the bottom line.
| Automation Technology | Quantifiable Benefit (Industry Average) | Impact on Epsilon Energy's OpEx |
|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance (IIoT) | Reduces unplanned downtime by 20-30% | Increases production days, securing cash flow. |
| Remote Monitoring (SCADA) | Cuts maintenance costs by nearly a third | Directly offsets the 39% OpEx increase seen in Q3 2025. |
| AI-Driven Analytics | Can cut process costs by up to 45% | Optimizes injection and flow rates in real-time for higher yield. |
Maturation of cost-effective carbon capture technologies is a must
Despite the growing regulatory and public pressure, Epsilon Energy's 2025 filings indicate a lack of a comprehensive plan to address climate change impacts. This is a material risk, especially as you expand your natural gas production.
The good news is that cost-effective Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies are maturing rapidly. For natural gas processing, the cost to capture concentrated $\text{CO}_2$ from feedgas is already in the range of \$20-\$50 per ton of $\text{CO}_2$. New, innovative technologies are even being reported to achieve capture for as low as \$26 per metric ton. The U.S. 45Q tax credit provides a significant financial incentive, making these projects economically viable today. You need to move from 'no plan' to feasibility studies immediately to de-risk your long-term gas assets.
Cybersecurity risks demanding higher IT spending to protect operational technology (OT)
The rapid digitalization that gives you the OpEx savings also creates a massive new vulnerability in your Operational Technology (OT) systems-the hardware and software that control your physical assets like pumps and valves. The entire energy industry's cybersecurity spending is projected to reach \$10 billion by 2025.
As a smaller operator with a TTM revenue of \$45.7 million, you can't afford a Colonial Pipeline-style attack. A single breach could shut down production, leading to millions in lost revenue and crippling reputational damage. Your IT spending must shift to prioritize the security of your remote monitoring and control systems. This means ring-fencing your OT network from the corporate IT network and investing in specialized security talent, not just general IT upgrades. This is defintely where a small, focused capital spend today prevents a catastrophic loss tomorrow.
Next Step: COO and CFO: Mandate a third-party OT network vulnerability assessment and draft a three-year budget for a dedicated OT cybersecurity program by year-end.
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - PESTLE Analysis: Legal factors
For a small-cap exploration and production (E&P) company like Epsilon Energy Ltd., legal and regulatory factors are not just compliance overhead; they are direct drivers of capital expenditure and can halt development. You need to map these risks to your cash flow, because a single regulatory change or adverse court ruling can significantly impact your drilling inventory and operating costs.
New EPA rules on flaring and venting potentially requiring $1.5 million in equipment upgrades.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is driving significant compliance costs through its new Methane Rule, specifically the New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) Subparts OOOOb and Emissions Guidelines (EG) Subparts OOOOc. These rules, which target new and existing oil and gas sources, mandate substantial reductions in methane and Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions.
The core of the challenge is the requirement for a 95 percent reduction in methane emissions from certain storage tanks and the mandate for continuous monitoring systems on flares and enclosed combustion devices. While the EPA granted an Interim Final Rule in July 2025 to extend certain compliance deadlines to 18 months, the capital investment is still a near-term certainty. For Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s multi-basin operations, which include the Marcellus and Permian, the estimated capital expenditure for installing the necessary Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) and upgrading control devices is approximately $1.5 million. This is a non-discretionary capital outlay that must be budgeted for the 2025-2026 period.
Furthermore, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) introduces a Methane Emissions Reduction Program, which imposes a fee on emissions above a certain threshold. For 2025, that fee is set to rise to $1,200 per metric ton of methane, creating a financial penalty for non-compliance that will directly hit the bottom line if the $1.5 million in upgrades is defintely delayed. That's a huge financial incentive to move fast.
Ongoing litigation risk related to mineral rights and lease disputes.
Epsilon Energy Ltd. faces persistent litigation risk common in the oil and gas sector, particularly concerning Joint Operating Agreements (JOAs) and mineral rights. This risk is twofold: legacy disputes and new regulatory hurdles impacting acquired acreage.
A prime example of a legacy dispute is the ongoing litigation with Chesapeake Appalachia LLC, concerning the interpretation of JOAs in the Marcellus Shale. This case, which has seen action in the Third Circuit, centers on Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s right to propose and operate new wells without Chesapeake Appalachia LLC's participation, directly challenging the economic viability of certain undeveloped reserves. Separately, the company's transformative acquisition of the Peak Companies in 2025 introduced new regulatory risk.
The acquisition terms included a contingent consideration of up to 2.5 million common shares, which are dependent on the ability to access acreage currently affected by a drilling permit moratorium in Converse County, Wyoming. If the legal or regulatory barriers to those permits are not resolved, the value of the acquired 40,500 net acres is compromised, creating a direct legal-to-valuation risk.
| Legal/Regulatory Risk Area | Impact on 2025 Operations | Financial/Operational Metric |
|---|---|---|
| EPA Methane Rule (OOOOb/c) | Mandatory equipment upgrades for flaring/venting. | Estimated $1.5 million capital expenditure. |
| Methane Emissions Fee (IRA) | Direct cost for emissions exceeding threshold. | Fee of $1,200 per metric ton in 2025. |
| Peak Acquisition Contingency | Access to new Powder River Basin acreage. | Up to 2.5 million common shares at risk. |
| Chesapeake Appalachia LLC Litigation | Right to drill new wells in Marcellus JOAs. | Potential loss of control over drilling inventory. |
Stricter Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards for field operations.
The financial stakes for workplace safety compliance have risen sharply in 2025. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) increased its maximum penalties effective January 15, 2025, making compliance failure a much more expensive mistake. For a company with field operations across multiple states-Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Pennsylvania-maintaining a unified, high-standard safety program is crucial.
The new penalty structure means that a single serious violation can now result in a maximum fine of $16,550, up from $16,131. More critically, a willful or repeated violation now carries a maximum fine of $165,514, an increase from $161,323. This 2.6% increase in maximum penalties compounds the regulatory burden, especially for smaller E&P operators where compliance costs per employee are already disproportionately high compared to larger peers. You must prioritize safety training and audit protocols. The cost of a few days of lost production and a six-figure fine far outweighs the investment in preventative measures.
Compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) for financial reporting remains complex.
As a publicly traded company on the NASDAQ, Epsilon Energy Ltd. must adhere to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), which governs internal controls over financial reporting (ICFR). For a company of this size, with an aggregate market value of non-affiliate common equity of approximately $90.9 million as of March 18, 2025, the fixed costs of SOX compliance are a significant drag on administrative expenses.
The complexity lies in Section 404, which requires management to assess and report on the effectiveness of ICFR, and for external auditors to provide an attestation. Integrating the financial reporting of the newly acquired Peak assets into the existing SOX framework is a major undertaking in the 2025 fiscal year. This integration requires:
- Mapping new business processes to existing controls.
- Testing controls for all Peak-related revenue and expense streams.
- Ensuring IT General Controls (ITGC) are consistent across the combined entity.
The legal and audit hours required to ensure a clean Section 404 attestation post-acquisition are substantial and non-negotiable. This is simply the cost of doing business as a public entity.
Epsilon Energy Ltd. (EPSN) - PESTLE Analysis: Environmental factors
Mandatory Reporting of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
The biggest near-term environmental factor for Epsilon Energy Ltd. is the new regulatory climate, not just the physical one. The Securities and Exchange Commission's (SEC) final rule on climate-related disclosures is now in effect for Large Accelerated Filers, fundamentally changing the reporting landscape for the 2025 fiscal year data.
This rule requires Epsilon Energy to disclose its material Scope 1 (direct) and Scope 2 (indirect from purchased energy) greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This disclosure is a massive shift, translating a purely environmental metric into a financial risk metric for investors. Honestly, if you're an investor, you need this data to compare Epsilon against its peers.
The compliance timeline for the 2025 fiscal year means Epsilon Energy must have a verifiable, auditable system in place now to accurately capture these emissions for their 2026 filings. This is not a future problem; it's a current-year operational cost and risk management challenge.
| SEC Climate Disclosure Requirement | Applicability to EPSN (FY 2025 Data) | Risk/Actionable Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 & 2 GHG Emissions Disclosure | Required if material (Highly likely for an E&P company) | Compliance Risk: Non-disclosure or inaccurate data will draw immediate regulatory and investor scrutiny. |
| Climate-Related Risk on Financial Statements | Required, including effects of severe weather events | Valuation Risk: Forces the company to quantify the financial impact of physical climate risks. |
| Implementation Start Date | Fiscal years beginning on or after January 1, 2025 | Immediate Action: Requires 2025 data collection and governance oversight. |
Focus on Reducing Scope 1 and 2 Emissions to Meet Stakeholder Targets
While Epsilon Energy Ltd.'s public disclosures, such as its 2024 Form 10-K, focus heavily on financial and operational metrics, there is a noticeable absence of specific, company-wide, quantitative Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions data or stated reduction targets for 2025 in the public domain. This lack of disclosure is itself a growing risk.
Stakeholders-from institutional investors like BlackRock to the wider public-are increasingly demanding specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) environmental targets. Without a clear commitment, Epsilon risks being screened out by Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) funds, which now manage trillions in assets. The pressure is real, even if the regulatory hammer (SEC disclosure) is the immediate driver.
Here's the quick math: if Epsilon Energy is a Large Accelerated Filer, they must report their Scope 1 and 2 emissions for 2025. If those numbers are high relative to peers in the Permian or Marcellus, and they have no plan to reduce them, their cost of capital will defintely rise. This is why peer companies are setting aggressive goals, like methane intensity reductions of 40% to 50% by 2030.
Increased Scrutiny on Water Usage and Disposal in Hydraulic Fracturing Operations
Epsilon Energy's core business relies on hydraulic fracturing (fracking) across its key operating areas, including the Marcellus Shale in Pennsylvania and the Permian Basin in Texas. This process is inherently water-intensive and creates significant volumes of flowback and produced water that require careful disposal.
The scrutiny on water usage and disposal is increasing from state regulators and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). In water-stressed regions like the Permian Basin, competition for fresh water is fierce. The industry trend is moving toward water recycling and the use of non-potable sources to mitigate this risk. Epsilon Energy's 2024 filing acknowledges the regulatory risk associated with hydraulic fracturing but does not publicly detail its water management strategy, recycling rates, or total water consumption volume for 2025.
The operational risks here are clear:
- Regulatory Fines: Improper disposal of produced water can lead to costly fines and operational shutdowns.
- Seismic Activity: Disposal wells, particularly in Oklahoma and Texas, are under intense scrutiny due to links with induced seismicity.
- Community Relations: High freshwater usage in arid regions damages the company's social license to operate (SLO).
Risk of Extreme Weather Events (Hurricanes, Floods) Disrupting Gulf Coast Infrastructure
While Epsilon Energy Ltd. is an onshore operator, its production and gathering systems are exposed to increasing climate volatility, particularly in Texas and Pennsylvania. The primary risk is not hurricane storm surge, but rather inland flooding and extreme heat.
The company's key assets are spread across: Marcellus (Pennsylvania), Permian Basin (Texas/New Mexico), Anadarko Basin (Oklahoma), and the newly acquired Powder River Basin (Wyoming). The Permian Basin in Texas faces chronic heat stress and acute flood risks. The broader Gulf Coast region, which houses the downstream processing and export facilities for much of the Permian's oil and gas, faces an expected average annual loss of $14 billion from climate hazards, a figure projected to rise to between $18 billion and $23 billion per year by the 2030 timeframe.
A major hurricane hitting the Texas coast, even if it misses Epsilon's inland wells, can shut down pipelines and refineries, which would immediately cut demand and realized prices for Epsilon's Permian production. This is an indirect but powerful financial risk.
The company must invest in resilience measures for its Auburn Gas Gathering System in Pennsylvania and its Permian infrastructure to mitigate risks from heavy rainfall and heat-related equipment failure.
Finance: draft a 13-week cash view by Friday, modeling three scenarios for gas price volatility.
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.
